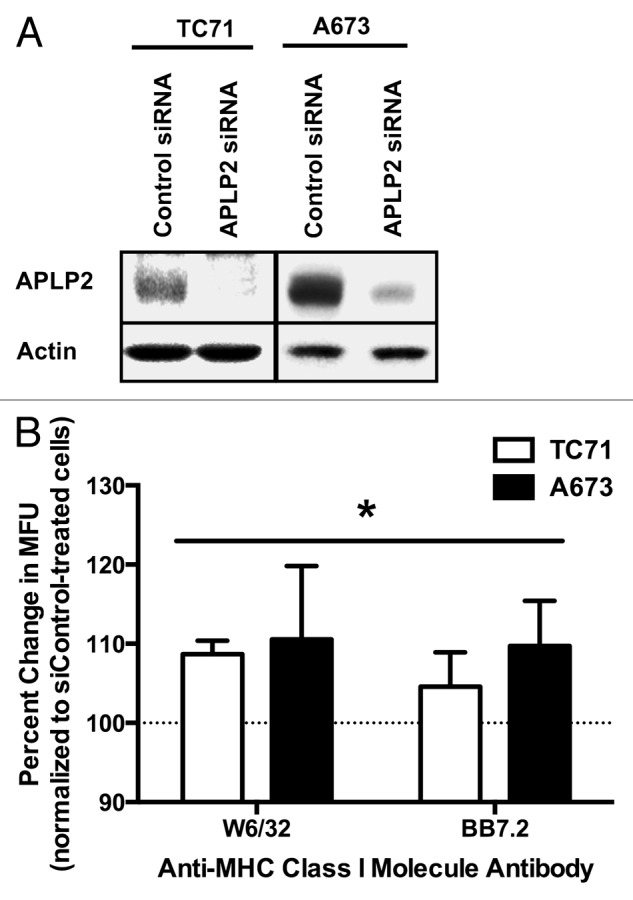
Figure 4. APLP2 downregulation increases MHC class I surface expression on EWS cells. (A-B) TC71 and A673 EWS cells were transfected with a siRNA pool targeting APLP2 or a non-targeting siRNA pool (as a negative control) for 48 h. (A) APLP2 downregulation upon transfection with APLP2-specific siRNA was confirmed by immunoblotting. Actin levels were monitored to ensure proper lane loading. (B) Surface-exposed MHC class I molecules were detected by flow cytometry on TC71 (black bars) and A673 (white bars) cells transfected with APLP2-specific or control siRNAs. The pan-human MHC-reactive W6/32 antibody and the allotype-specific BB7.2 antibody were used to detect MHC class I molecules and HLA-A2 molecules, respectively. The bar graphs depict the percent change (means ± SD) in MHC class I-dependent fluorescence (in terms of mean fluorescence units, MFU) elicited with APLP2-specific siRNAs (with cells transfected with control siRNA represented by 100%, as indicated by the dashed line). Individual MFUsiAPLP2/MFUsiControl results were obtained from paired samples, and data from 3 independent experiments were pooled. For each cell line and each antibody, siAPLP2 transfection (compared to siControl transfection) resulted in a significantly higher surface MHC class I level. Statistical significance was determined by means of unpaired Student t-test (*p < 0.05). The values used for derivation of this graph are presented in Table S1.
