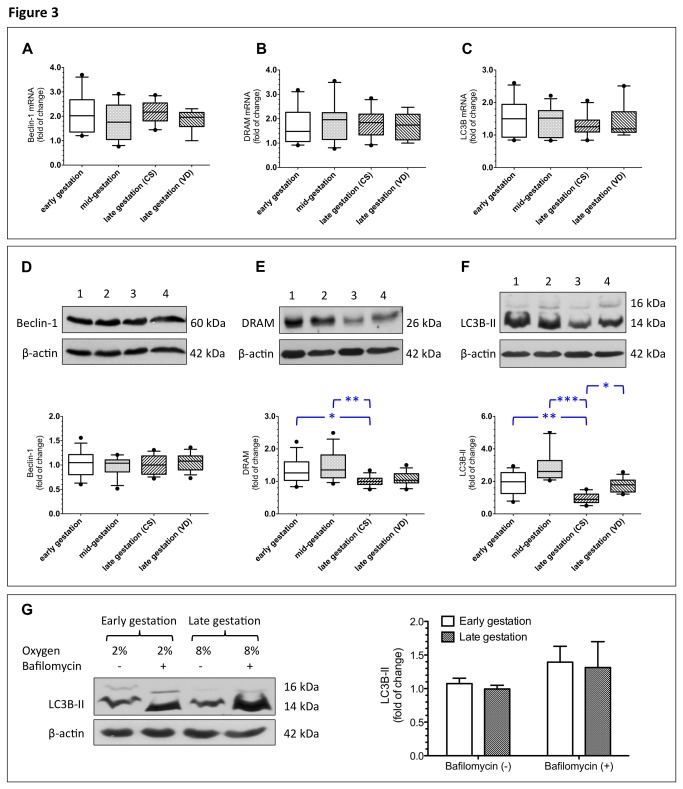
Figure 3. Beclin-1, DRAM, and LC3B levels and autophagic flux in villous tissues from various stages of gestation and different modes of delivery.
In a total of 40 samples representing different gestational stages and modes of delivery, BECN1, DRAM, and LC3B mRNA were continuously expressed in villous tissues throughout gestation and there were no significant differences in the levels of BECN1, DRAM, and LC3B mRNA between villous tissues of different stages of gestations and between women with different modes of delivery (A–C). On the other hand, levels of beclin-1 remained constant throughout gestation (D), while significantly higher levels of DRAM and LC3B-II were noted in villous tissues from early and mid-gestation than in those of term placentas obtained from elective CS (E–F). Furthermore, women with VD had higher levels of LC3B-II than did those with CS (F). CS, cesarean section; VD, vaginal delivery. A total of 10 placentas from early gestation (7–12 weeks), 10 from mid-gestation (13–28 weeks), 10 from late gestation with CS (38–39 weeks), and 10 from late gestation with VD (38–40 weeks) were used for analysis. β-actin was used to normalize loading variability. Lane 1, villous tissues from early gestation; lane 2, villous tissues from mid-gestation; lane 3, villous tissues from late gestation with CS; and lane 4, villous tissues from late gestation with VD. Data are presented as median and interquartile range and plotted as box and whisker plots (box = interquartile range, whiskers = 90th and 10th percentiles). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, and ***P < 0.001, compared to villous tissues of late gestation with CS (A-F). Villous explants prepared from early gestation and from term pregnancy were cultured under 2% and 8% oxygen concentrations, respectively, with or without bafilomycin A1. Villous explants from early and late gestation showed similar levels of LC3B-II when exposed to bafilomycin A1, indicating that these two groups of tissues had comparable rates of autophagic flux under physiological oxygen concentrations. Data are presented as mean ± S.D. from 5 individual experiments (G).