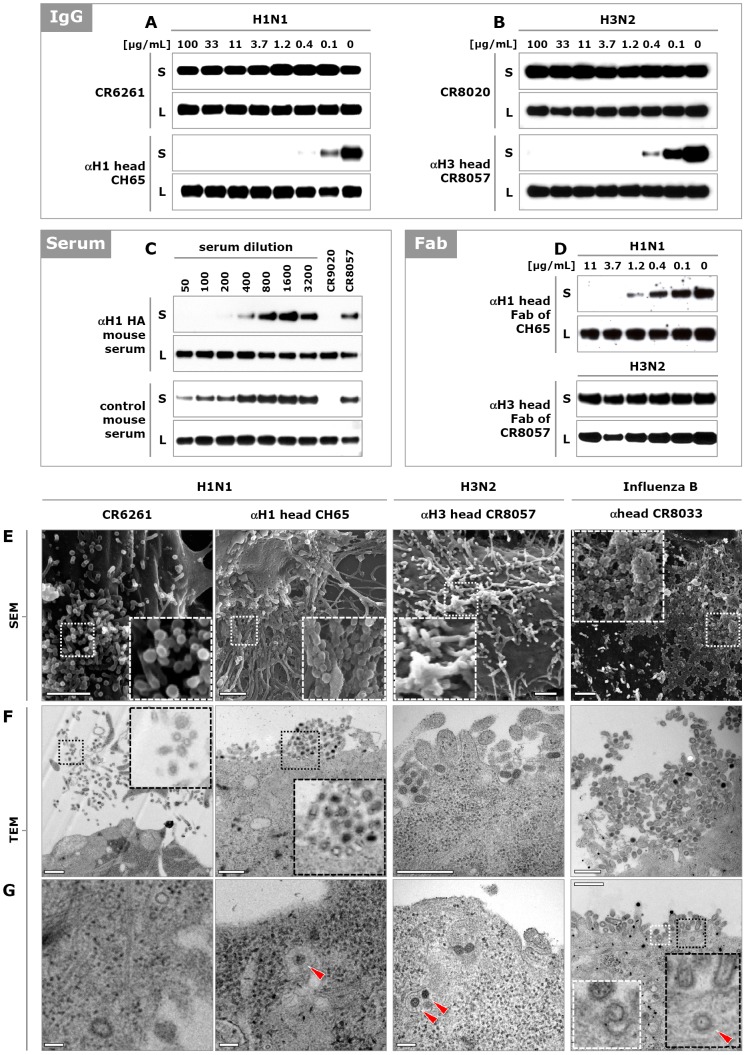
Figure 4. HA head binding antibodies inhibit influenza virus egress.
(A) Calu-3 cells were infected with A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 (H1N1) and 3 hours later stem-binding antibody CR6261 or head-binding antibody CH65 was added. Twenty hours later, the amounts of HA present in the cell supernatant (S) and lysate (L) were analyzed by Western blot (HA0 band shown). (B) As in (A) except that cells were infected with A/Wisconsin/67/2005 (H3N2) virus and stem- and head-binding antibodies CR8020 and CR8057, respectively, were used. (C) Naïve mice were immunized and boosted twice with DNA encoding the HA of influenza A/Brisbane/59/2007 (H1N1) virus. Serum was collected and added to MDCK cells 3 hours after infection with the same virus. The amount of newly produced particles in culture supernatants and cell lysates were analyzed 20 hours later by Western blot (HA0 band shown). As positive and negative controls 1 µg/mL of CR9020 and CR8057 were included, respectively. (D) Fab fragments of head-binding antibodies CH65 and CR8057 were added 3 hours after infection of MDCK cells with A/Puerto Rico/8/1934 (H1N1) and A/Wisconsin/67/2005 (H3N2) virus, respectively, and 20 hours later the amounts of HA present in the supernatant were analyzed as above. (E) SEM images of the surface of MDCK cells infected with influenza A/New Caledonia/20/1999 (H1N1), A/Wisconsin/67/2005 (H3N2), or influenza B/Florida/04/2006 virus and subsequently incubated (from 3 hours post infection) with CR6261 (50 µg/mL, 333 nM), CH65 (10 µg/mL, 67 nM), CR8057 (0.5 µg/mL, 3 nM) or CR8033 (2.5 µg/mL, 17 nM) respectively. Representative images of three independent experiments are shown. Scale bar 1 µm. (F and G) As in (E) except TEM images of ultrathin sectioned MDCK cell (re-internalized particles indicated with red triangles). Scale bar in (F) 500 nm and in (G) 100 nm.