Figure 2.
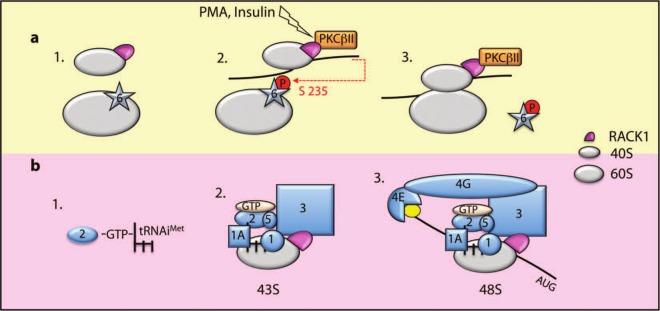
Schematic representation of RACK1’s putative role in translation initiation. (A) RACK1 and the antiassociation factor eIF6 bind 40S and 60S, respectively (1). RACK1 recruits PKCβII to the ribosome, and PKCβII phosphorylates eIF6 on serine 235 (2). Release of phosphorylated eIF6 allows 80S formation on the mRNA (3). (B) The ternary complex (eIF2-GTP-tRNAiMet) (1) is recruited to 40S with a multimeric complex composed of eIF1A, eIF1, eIF5, and eIF3. eIF3 binding to RACK1 stabilizes the ternary complex on the ribosome (2). The 43S complex is then recruited to the mRNA and stabilized through an eIF3-eIF4G interaction (3). The 48S complex scans the mRNA to reach the initiation codon (AUG).
