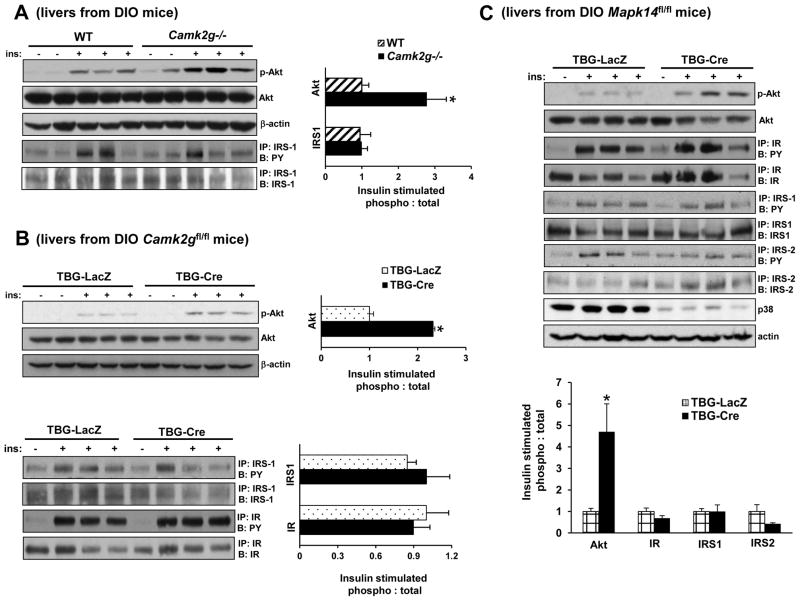
Figure 3. Deletion of CaMKII or p38α Improves Insulin-induced Akt Phosphorylation in Obese Mice.
(A) DIO Camk2g−/− or WT mice were fasted for 6 h and then injected with 1.5 IU/kg insulin through the portal vein. Total liver extracts were then assayed for p-Akt, total Akt, and β-actin by immunoblot or immunoprecipitated (IP:) for IRS-1 and then assayed by immunoblot (B:) for IRS-1 or for phospho-Tyr (PY). Densitometric quanti cation of the immunoblot data is shown in the graph (*p < 0.05; mean ± S.E.M.). (B) As in (A) except that DIO Camk2gfl/fl mice treated with AAV-TBG-LacZ or AAV-TBG-Cre were used and p-IR was also assayed by IP/B (*p <0.05; mean ± S.E.M.). (C) As in (B) except that DIO Mapk14fl/fl mice were used, and p-IRS-2 was also assayed by IP/B (*p <0.05; mean ± S.E.M.). See also Figure S2–3.