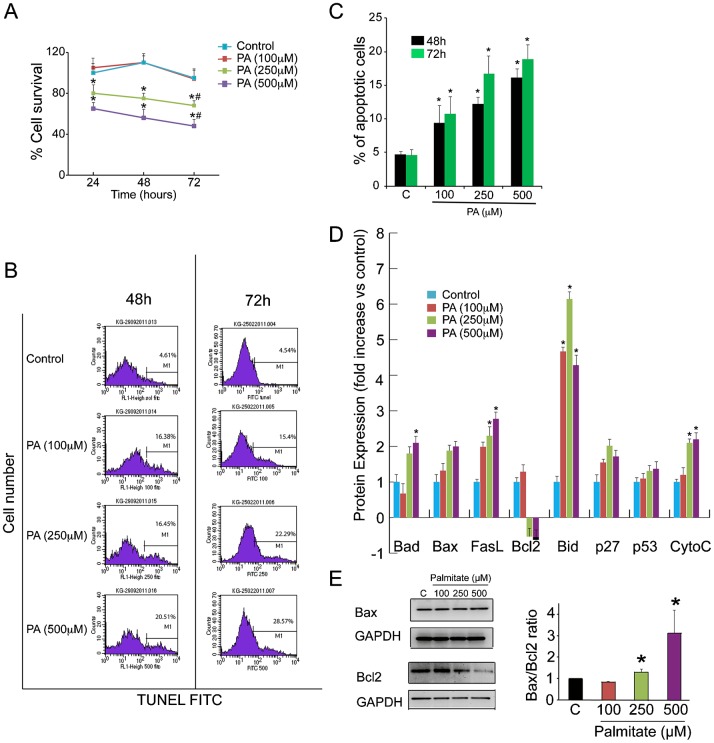
Fig. 1. PA induces cell death in human osteoblasts in a dose-dependent manner.
(A) Human osteoblasts (Ob) were treated with PA (100, 250, and 500 µM) for 24, 48 and 72 h for cell survival assay (MTS). Data are mean percentage of three independent assays. The percentage absorbance of treated Ob was expressed relative to absorbance of control Ob, which was set at 100%. *P<0.001, vs. vehicle-treated control; #P<0.05 vs. % at 24 h for each condition. (B and C) Ob were treated with PA (100, 250 and 500 µM) for 48 and 72 h. Ob were analysed for the relative percentage of apoptotic cells was measured by TUNEL. The data are representative of three different experiments and are shown as mean±SD. *P<0.05 vs. vehicle-treated control. (D) Proteomic analysis of apoptotic pathways in Ob treated with either PA (100, 250 and 500 µM) or vehicle (control) for 48 h. Results were reported as mean ± SEM for at least three analyses for each sample. (E) Western blot of Ob treated with PA (100, 250, and 500 µM) demonstrating Bax and Bcl2 expression at 48 h. The right hand panels show quantification of the Bax/Bcl2 ratio against GAPDH using image J software. *P<0.05 vs. vehicle-treated control.