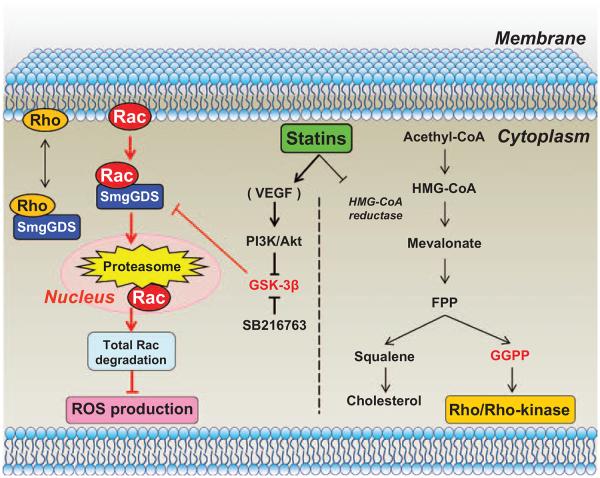
Figure 6.
Novel mechanisms of the pleiotropic effects of statins. The present study demonstrates that regular-dose statins enhance small GTP-binding protein GDP dissociation stimulator (SmgGDS) expression through glycogen synthase kinase (GSK)-3β inhibition via phosphoinositide-3-kinase (PI3K)/Akt pathway, and that SmgGDS transports Rac1 to the nucleus, where Rac1 is degraded by the nuclear proteasome with resultant reduced reactive oxygen species (ROS) production (left). In contrast, high-dose statins exert inhibitory effects on the Rho/ Rho-kinase pathway as previously demonstrated (right). FPP indicates farnesyl pyrophosphate; GGPP, geranylgeranyl pyrophosphate; HMG-CoA, 3-hydroxy-3-methylglutaryl-coenzyme A; and VEGF, vascular endothelial growth factor.