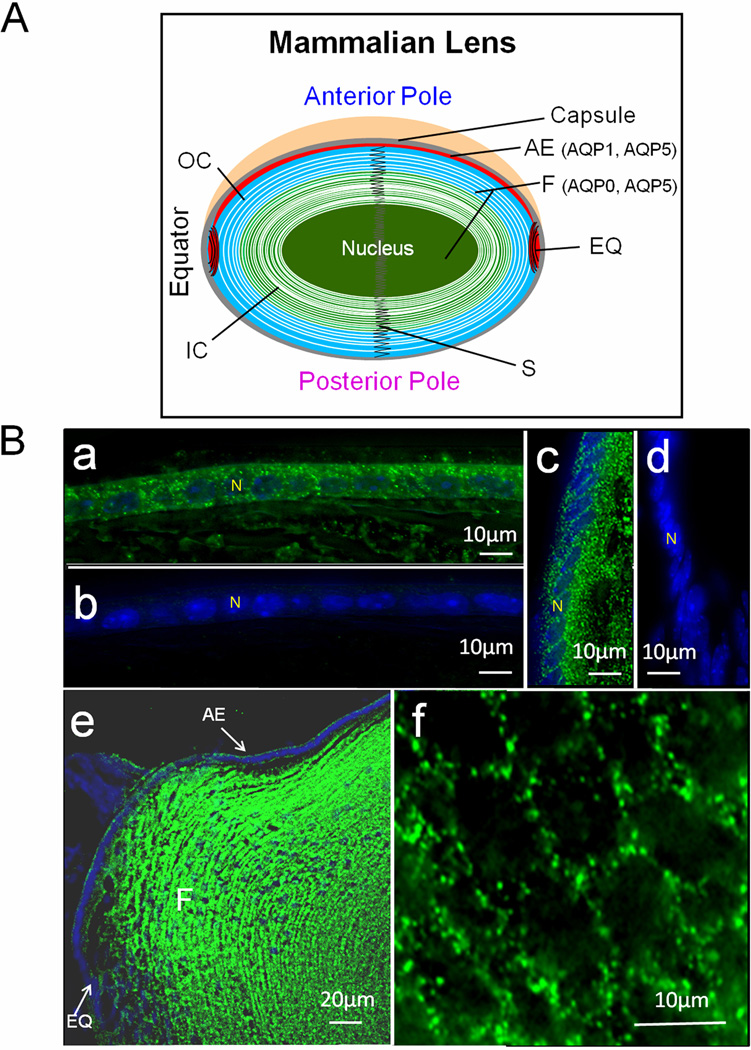
Fig. 1.
A. Schematic representation of the expression patterns of AQP0, AQP1 and AQP5 in adult mouse lens. B. Immunostaining using anti-AQP5 antibody in lens cryosections. a: WT epithelial cells; b: AQP5-KO epithelial cells; c: WT lens equatorial region showing AQP5 in epithelial and differentiating fiber cells; d: AQP5-KO equatorial epithelial cells; e: Sagittal section, WT lens epithelial and fiber cells showing immunoreactivity to anti-AQP5 antibody; f: Cross-sectional view of WT cortex fiber cells showing AQP5 expression. a–f: FITC-conjugated secondary antibody; green, antibody binding; blue, nuclear staining by DAPI. White arrows – antibody binding. AE, anterior epithelial cells; EQ, equatorial epithelial cells; F, fiber cells; IC- Inner cortex; N-nucleus; OC- outer cortex; S- suture.