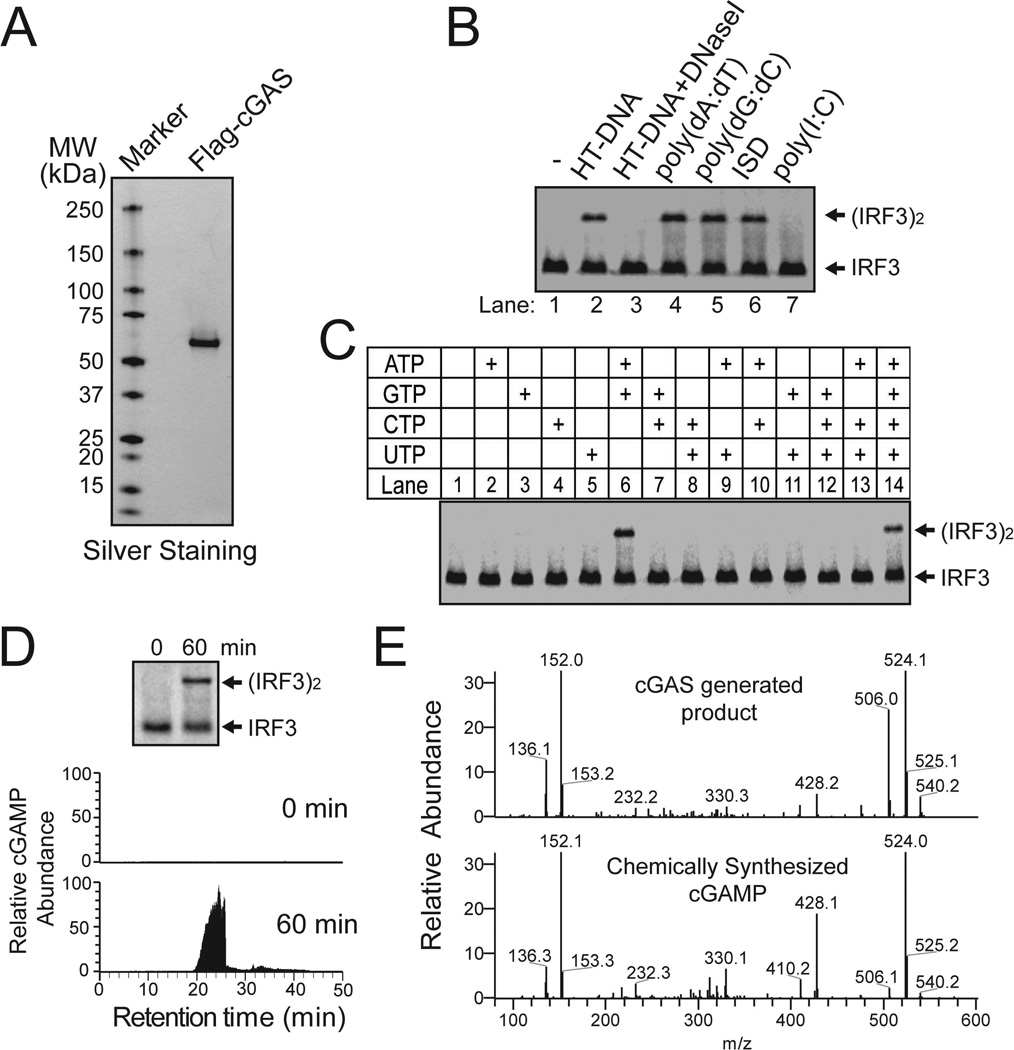
Figure 4. DNA-dependent synthesis of cGAMP by purified cGAS.
(A) Silver staining of Flag-h-cGAS expressed and purified from HEK293T cells. (B) Purified Flag-h-cGAS as shown in (A) was incubated with ATP and GTP, in the presence of different forms of nucleic acids as indicated. Generation of cGAMP was assessed by its ability to induce IRF3 dimerization in Raw264.7 cells. (C) Similar to (B), except that reactions contained HT-DNA and different combinations of NTP as indicated. (D) Similar to (B), except that WT and mutant cGAS proteins were expressed and purified from E. coli and assayed for their activities at indicated concentrations. (E) Purified m-cGAS from E coli was incubated with ATP, GTP and DNA for 0 or 60 min, and the production of cGAMP was analyzed by IRF3 dimerization assay (top) and mass spectrometry using SRM (bottom).