Figure 1. Overview of study design.
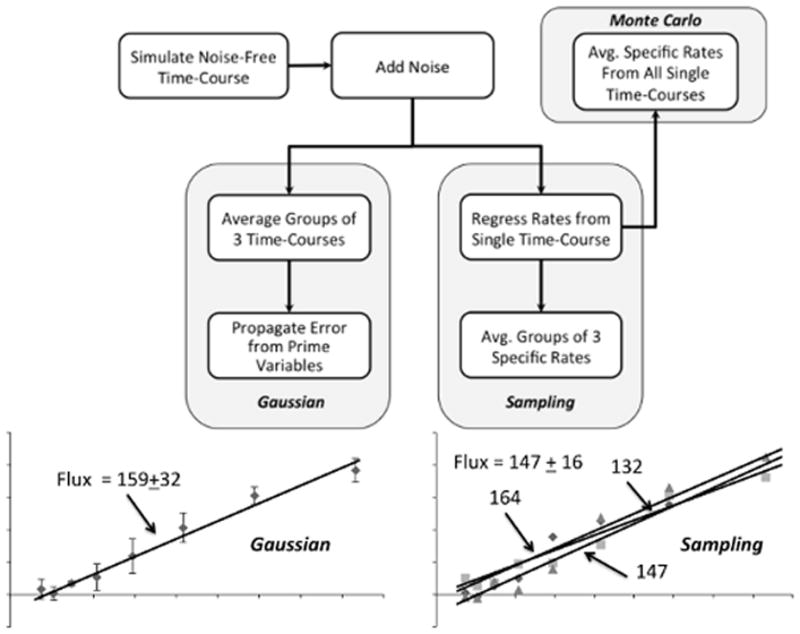
A noise-free time course was simulated using the parameter values listed in Table I. Normally distributed random errors were added to the noise-free time course to generate 9999 replicates. The replicates were grouped into 3333 simulated experiments, each with n=3. The simulated experiments were analyzed using either the Gaussian or Sampling approach to estimate specific rates and uncertainties. Monte Carlo estimates of the true parameter values and uncertainties were determined by computing the average and standard deviation of specific rates regressed from all 9999 time courses. An example is provided to illustrate how the Gaussian approach applies a single regression based on the average measurements from each simulated experiment, whereas the Sampling approach averages the rate parameters from n replicate regressions to estimate the final specific rate and its associated uncertainty.
