Figure 2.
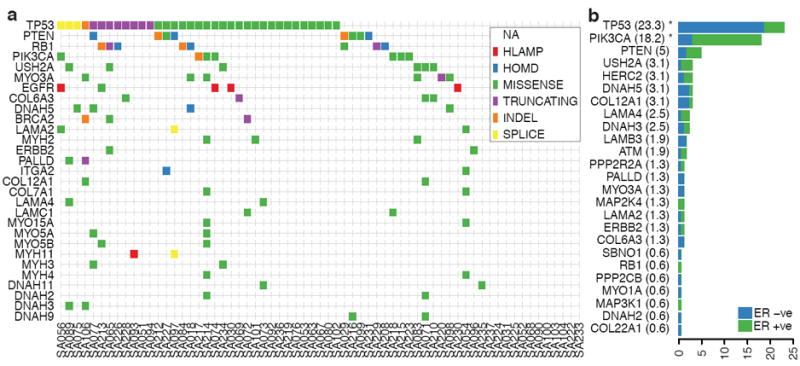
Population patterns of co-occurrence and mutual exclusion of genomic aberrations in TNBC. (a) Case-specific mutations in known driver genes, plus genes from integrin signaling and ECM related proteins (laminins, collagens, integrins, myosins and dynein) derived from all aberration types: high-level amplifications (HLAMP), homozygous deletions (HOMD), missense, truncating, splice site and indel somatic mutations are depicted in genes with at least two aberrations in the population. (b) Distribution of somatic mutations in 25 genes across all exons of 159 additional breast cancers (relative proportion of ER+ cases in green, and ER- in blue), shown as a percentage of cases with one or more mutations.
