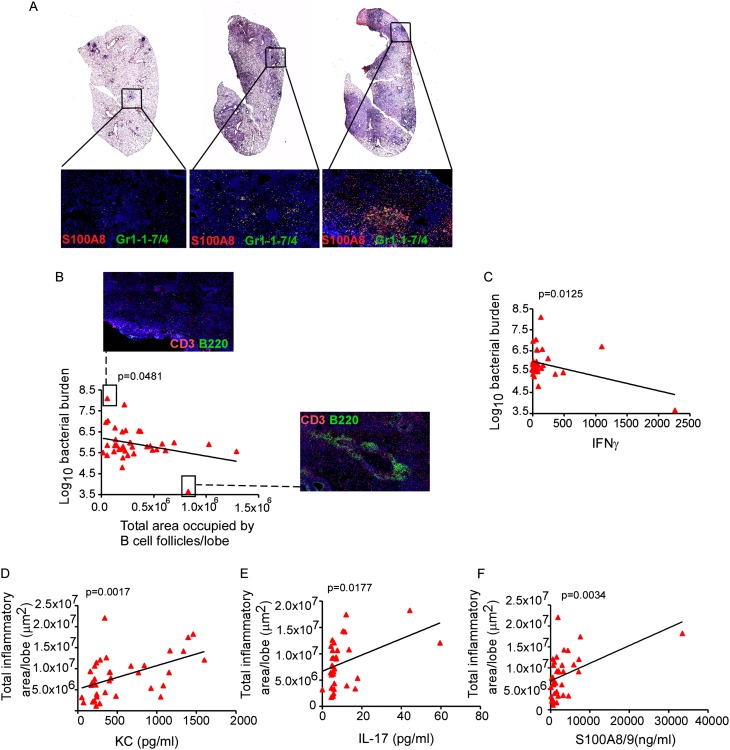
Figure 3.
Inflammation in Mycobacterium tuberculosis (Mtb) infected genetically diverse Diversity Outbred (DO) mouse population is associated with increased IL-17 production and S100A8/A9 proteins. (A) Genetically diverse mice from DO strain were aerosol infected with approximately 100 CFU of Mtb H37Rv and on Day 60 postinfection, formalin-fixed paraffin embedded (FFPE) lung sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin or analyzed by immunofluorescence using antibodies specific for S100A8 (red) and Gr1-1-7/4 (green). FFPE lung sections were also analyzed by immunofluorescence using antibodies specific for B220 (green) and CD3 (red), and the total area occupied by B-cell follicles per lobe quantified using the morphometric tool of the Zeiss Axioplan (Carl Zeiss, Oberkochen, Germany) (4 × 4 mosaic, ×200 original magnification). Lung CFU was determined by plating. Linear correlation analysis between total area occupied by B-cell follicles per lung lobe and bacterial burden (B) and lung IFN-γ levels and bacterial burden (C) was performed using GraphPad Prism. A representative image demonstrating absence of B-cell follicles in a mouse exhibiting the highest Mtb bacterial burden and a representative image showing well-formed B-cell follicles in a mouse exhibiting the lowest Mtb burden is also shown (×100 original magnification). Total area occupied by inflammatory lesions per lobe was quantified in the Mtb-infected hematoxylin and eosin–stained FFPE lungs using the morphometric tool of the Zeiss Axioplan microscope. Lung protein levels of keratinocyte chemoattractant (KC) (D), IL-17 (E), and S100A8/A9 proteins (F) were measured and linear regression analysis was determined using GraphPad Prism. The data points represent values from 37 mice (A–F).