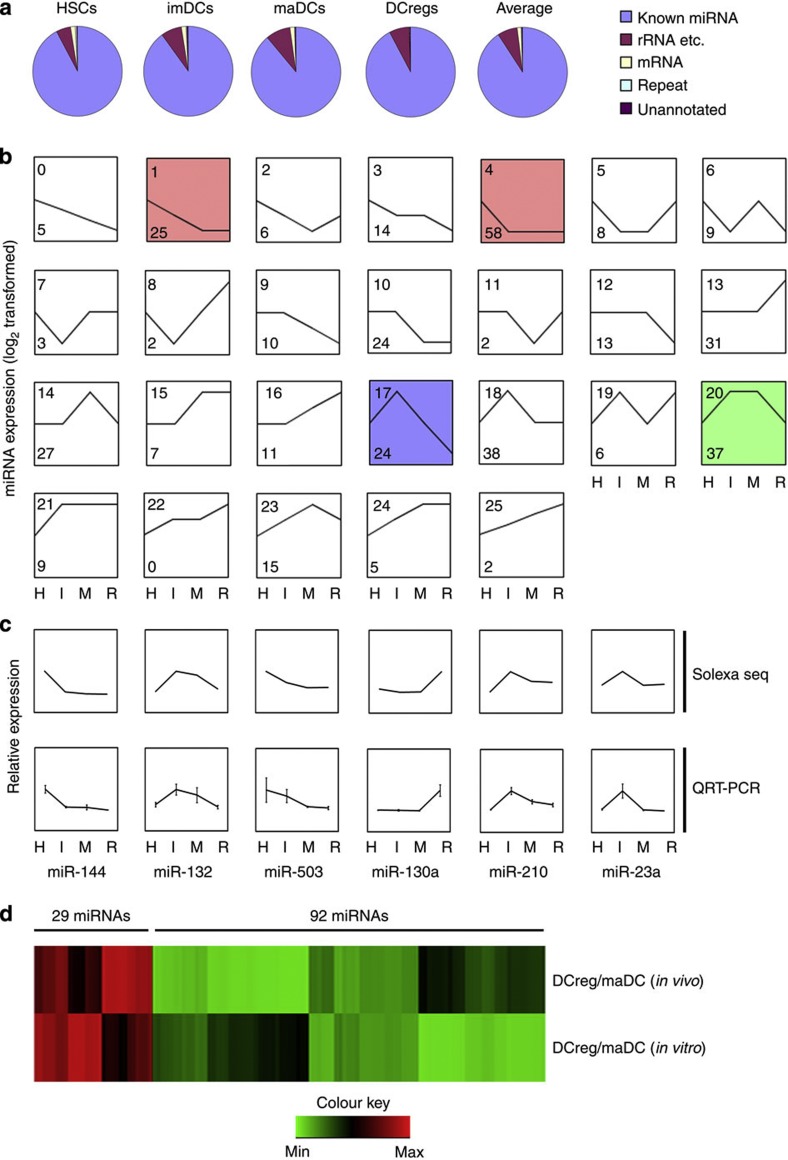
Figure 1. Clustering of 391 differentially expressed miRNAs during DC development and differentiation.
(a) Each small RNA sequence was assigned with a unique annotation and classified small RNAs into different categories such as known miRNA, rRNA and so on (rRNA, tRNA, snRNA, snoRNA), repeat (LINE, SINE, LTR), mRNA (exons/introns) and unannotated small RNAs. (b) The trend of 391 miRNAs was generally divided into 26 clusters according to their dynamic expression patterns among the four cell stages. Numbers on top left corner indicate the cluster number. Number on down left corner indicated the number of miRNAs in each cluster. The coloured clusters indicated significantly enriched ones by miRNAs (cluster 4 (red) P=0.0015; cluster 20 (green) P=0.0005; cluster 1 (red) P<0.00001; cluster 17 (blue) P=0.0001) (Fisher exact test). Three other expressions were normalized to the highest one in four stages firstly, and then all expressions were log2-transformed. (c) Six miRNAs were tested by qRT–PCR and compared with the results from Illumina sequencing. Three other expressions were normalized to the highest one in four stages firstly, and then all expressions were log2-transformed. (d) A total of 121 miRNAs with the same alteration pattern in process (maDCs-DCreg) in vitro and in vivo were selected. Expression of variation (fold) of each miRNAs between DCreg and maDCs was log-transformed and hierarchically clustered. H, HSCs; I, imDCs; M, maDCs; R, DCreg.