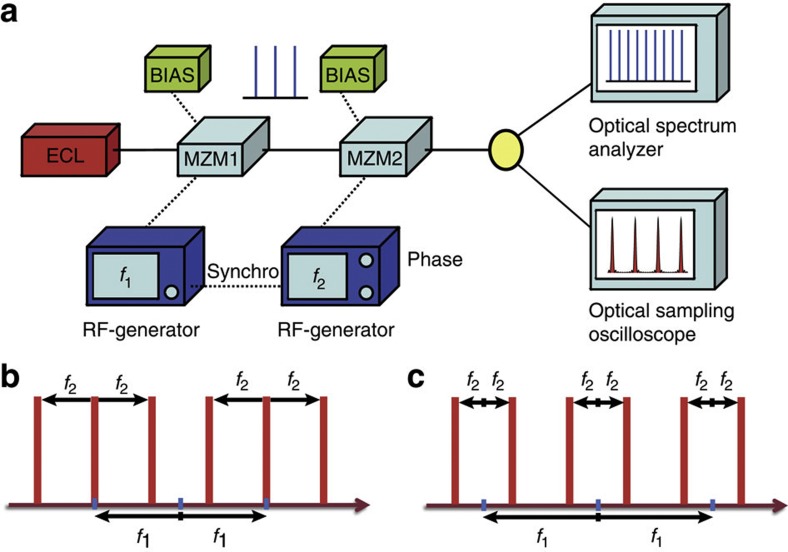
Figure 4. Basic experimental implementation.
(a) Proof-of-concept set-up. Solid and dashed lines describe optical and electrical connections, respectively. An external cavity laser (ECL) generates a narrow linewidth continuous wave light at 1,550 nm. MZM1 generates spectral lines separated by a frequency f1. Then, MZM2 re-modulates these seeding components with a frequency f2. RF power and DC bias in both MZMs are adjusted so that all lines result with the same amplitude and phase, and additional sidebands are highly suppressed. An undistorted waveform is only obtained with a proper adjustment of the relative modulating phase, and therefore both RF generators have been synchronized using a common time base. (b) Generation of a frequency comb with N=6 lines. MZM1 is driven with a frequency f1 and operates in carrier suppression mode, so that MZM2 re-modulates the two seeding lines, with no carrier suppression, at a frequency f2=Δf. (c) Second option to generate a comb with N=6 spectral lines; in this case, MZM1 is driven with a frequency f1 (no carrier suppression), while MZM2 re-modulates the three seeding components, in carrier suppression mode, at a frequency f2=f1/4=Δf/2.