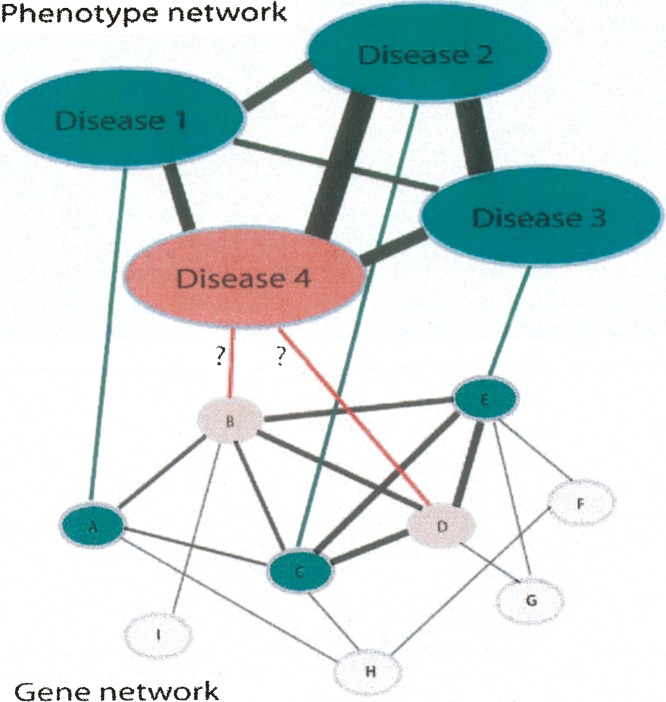
Figure 2.
A gene-phenotype network. Shown is a combined gene–gene, gene–phenotype, and phenotype–phenotype interaction network. In this hypothetical example, diseases 1, 2, and 3 have known causative genes (genes A, C, and E, respectively), and are all phenotypically related to disease 4, which lacks an identified causative gene. If the known causative genes are functionally closely related, as in this case, then candidate genes (genes B and D) can be hypothesized for disease 4 due to their close functional relationships to the known genes of the phenotypically related diseases. Black lines of varying thickness indicate the degree of phenotypic and functional similarity between diseases and genes, respectively. Reproduced from Oti and Brunner (2007) and reprinted with permission from Blackwell Publishing Ltd. © 2007 (www.blackwell-synergy.com).