Figure 3. Vangl2 functions in floor plate cells in r4 to regulate FBM neuron migration.
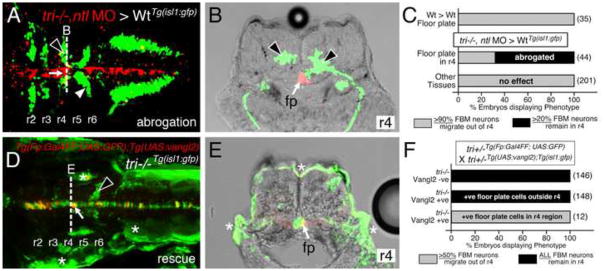
Panels A, D show dorsal views of 36 hpf (A) and 48 hpf (D) Tg(isl1:GFP) host hindbrains, and panels B, E show cross-sections at the levels indicated by the broken lines. Vangl2 mutants are indicated as tri−/− throughout. (A, B) Presence of vangl2 mutant donor cells in the floor plate (fp) in r4 (arrows) of a wildtype host can abrogate (partially block) the migration of some host FBM neurons (black arrowheads) out of r4. A large number of host neurons (white arrowhead) migrate caudally. (C) Quantification of vangl2 mutant > Wt transplantation data. Number of embryos in parentheses. (D, E) Floor plate-specific expression of vangl2 (arrows) in a vangl2 mutant completely rescues the migration of host FBM neurons (arrowhead). Gal4+ve floor plate cells are green, Myc-Vangl2+ve cells are red or yellow. Asterisks indicate Gal4FF-induced GFP expression in otic vesicle, trunk muscles, and skin. Many GFP-expressing cells are Myc-Vangl2-ve (and vice versa) probably due to independent and variable silencing of the UAS:GFP and UAS:Myc-vangl2 transgenes integrated at different sites. (F) Quantification of Gal4-UAS rescue data. Number of embryos in parentheses. fp, floor plate.
