Fig. 4.
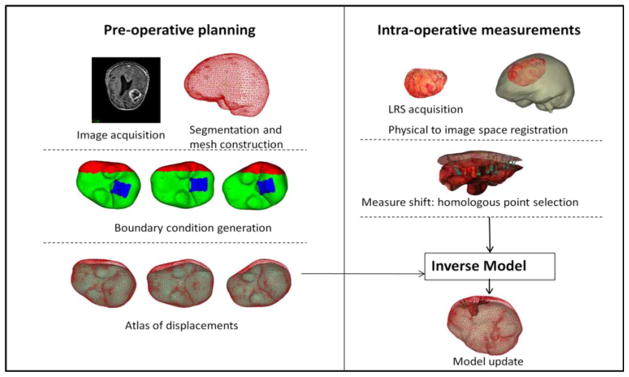
Schematic showing the overall procedure for model updated image-guided neurosurgery. Workflow is broadly divided into preoperative and intraoperative phases. Most time intensive steps are done in the preoperative phase, i.e., image segmentation and mesh construction. Boundary conditions for each deformation type and generation of model solutions to form the atlas are also done preoperatively. Some representative displacement boundary conditions are shown—with blue region being the fixed brainstem, red represents the stress free region, and green the slippage boundary conditions. Dural septa (not shown in the figure) are included in the model by assigning them the slippage boundary condition. Intraoperative phase consists of sparse data collection (laser range scans), registration of those scans to image space and obtaining measured shift through homologous points on the pre- and postresection scans. In the last step, those measurements are used to fit the displacement atlas using an inverse model to obtain the final model updated results.
