Fig. 5.
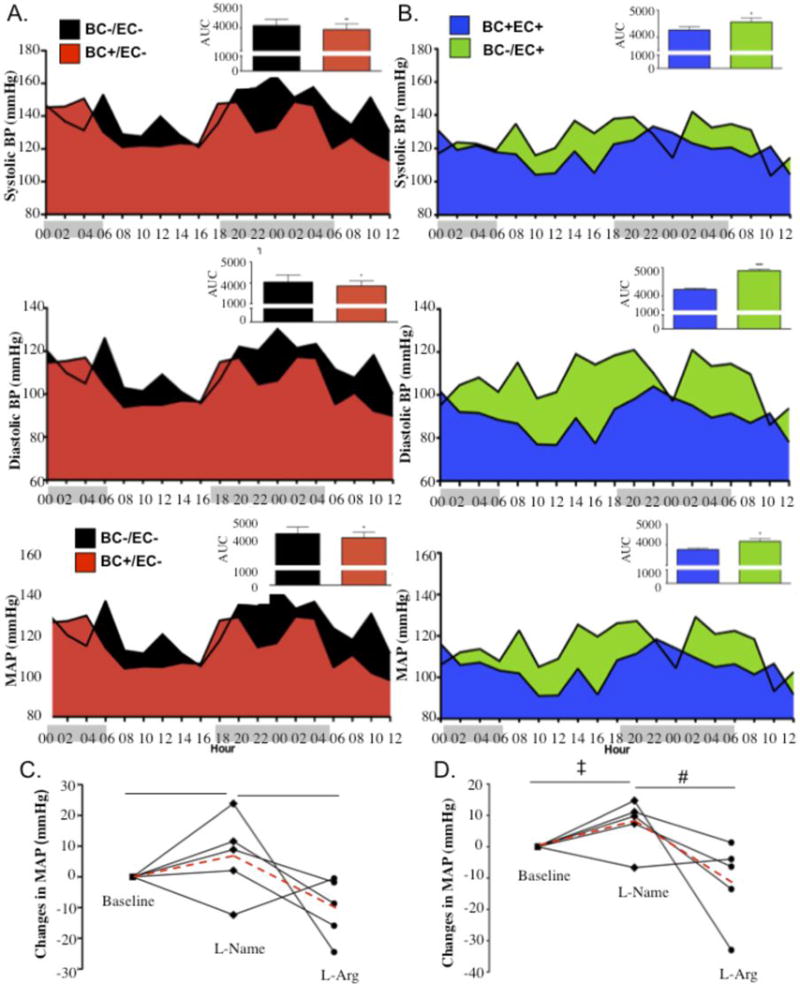
Blood pressure lowering effects of eNOS competent blood are responsive to L-NAME and L-Arginine (L-Arg) treatments. Thirty-six hour radiotelemetry-detected baseline BPs in (A) BC−/EC+ (n=3) versus BC+/EC+ (n=4) (systolic: p=0.0171, diastolic: p<0.0001, MAP: p=0.0011) and (B) BC+/EC− (n=3,) versus BC−/EC− (n=4) (systolic: p=0.0112, diastolic: p=0.0036, MAP: p=0.0056), with group averages calculated for each 2 hour interval and area under the curve (AUC) by 2-way ANOVA. Comparisons of moving averages, assessed by 2-way ANOVA, were also statistically significant (p<.0001). X-axis depicts hours of darkness (gray shade) versus hours of light (white shade) (C, D) Change in radiotelemetry-detected MAP (mmHg) in (C) Harvard BC+/EC− chimeras (n=5) and (D) UNC BC+/EC− chimeras (n=5) after oral treatment with L-NAME or L-Arginine. Blood pressure data for individual animals shown as solid lines; group averages shown as dashed red line. ‡ denotes p<0.05 for L-NAME versus baseline. # denotes p<0.05 for L-Arginine versus L-NAME. * denotes p<0.05 using Student’s t-test.
