Figure 7.
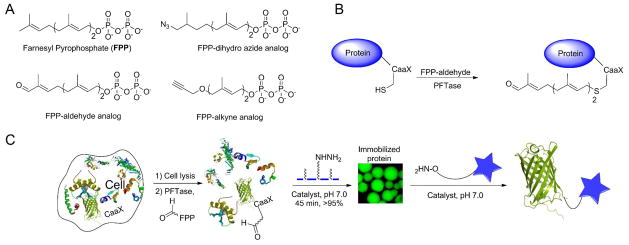
(A) Structures of farnesyl diphosphate (FPP), farnesyl dihydro azide diphosphate (FPP-dihydro azide) farnesyl aldehyde diphosphate (FPP-aldehyde) and farnesyl-alkyne diphosphate (FPP-alkyne) as examples of FPP analogues. (B) Schematic representation of prenylation of a protein containing a CaaX-box positioned at its C-terminus with aldehyde-containing analogue (FPP-aldehyde) to yield the prenylated product. (C) Chemoenzymatic site-specific tagging of proteins by FPP-aldehyde using PFTase followed by capture of the aldehyde-functionalized protein in the crude cell lysate via hydrazide-functionalized beads. The immobilized protein is then released into solution using aminooxy-containing reagents to yield fluorescently labeled or PEGylated protein.
