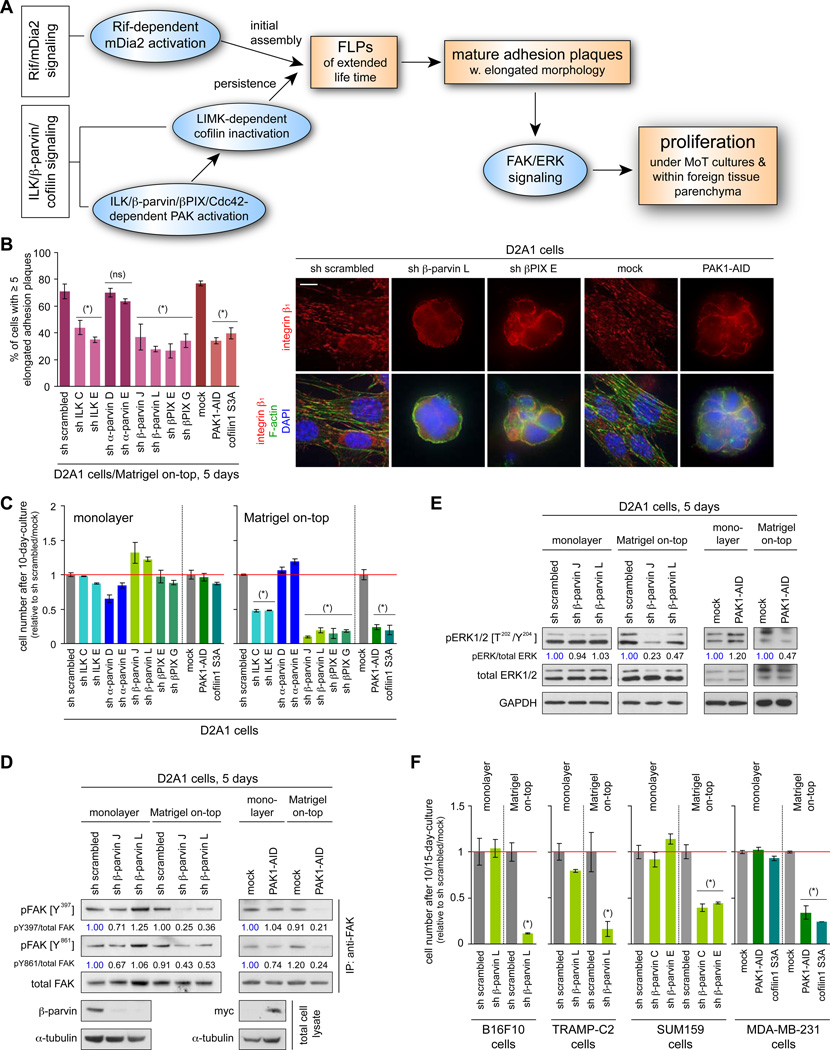
Figure 4. in vitro effects of ILK/β-parvin/cofilin signaling manipulation.
(A) Cell-biological and biochemical events that drive cell proliferation in MoT culture and within the lung parenchyma.
(B, C) Role of ILK/β-parvin/cofilin signaling in adhesion plaque assembly and proliferation. The D2A1 cells were manipulated as indicated, with which the rate of mature adhesion plaque assembly in MoT culture (B) and the cell numbers after 10 days of monolayer or MoT culture (C) were determined. Bar = 10 µm.
(D, E) β-parvin/PAK signaling and FAK/ERK activation. Values represent the intensities of pFAK (pERK) bands relative to that of the corresponding total FAK (ERK) band.
(F) ILK/β-parvin/cofilin signaling and proliferation in various cell types. Indicated cell types were manipulated to block ILK/β-parvin/cofilin signaling, with which the cell numbers after 10 (15 for MDA-MB-231) days of monolayer/MoT cultures were determined.
Values = means ± SD (n = 3: B, C, F). (*) p < 0.02, (ns) p > 0.1 (vs sh scrambled/mock). See also Figure S4.