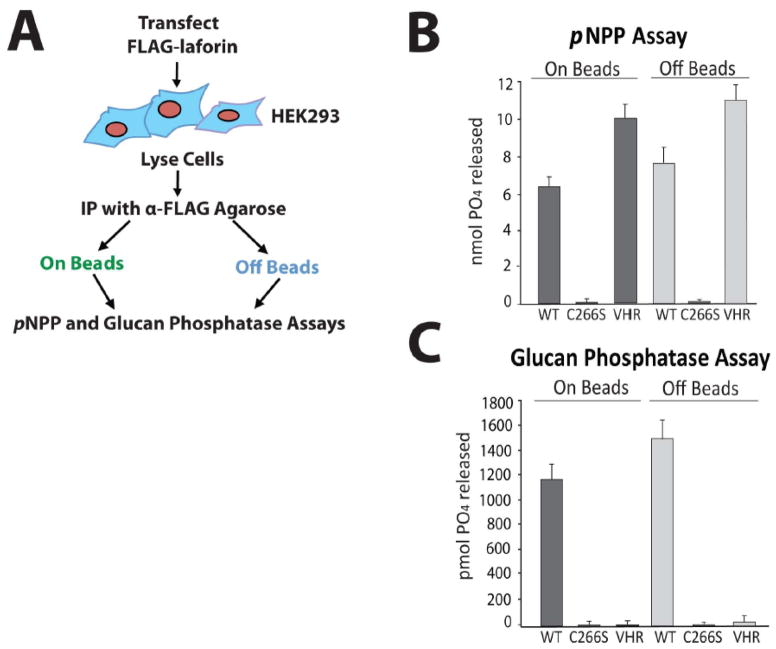
Figure 1. Laforin exhibits phosphatase activity both bound to and free of the antibody-agarose complex.
A. Schematic of experimental design. Before attempting to test endogenous laforin, we first optimized our experimental conditions using overexpressed laforin. We immunoprecipitated FLAG-laforin and assessed its pNPP and glucan phosphatase activity both bound to and free of the FLAG antibody-agarose complex (“on beads” and “off beads”) in order to determine if antibody binding to laforin inhibits activity. B. pNPP assay of immunoprecipitated FLAG-laforin. FLAG-tagged human wild-type laforin, catalytically inactive C266S laforin, and wild-type VHR were expressed in HEK293 cells and immunoprecipitated with α-FLAG agarose. VHR, a DSP that acts upon protein substrates and not glucan substrates, was included as a control. Immunoprecipitated proteins were either left bound to the antibody-agarose complex (“on beads”) or eluted from the complex using FLAG peptide (“off beads”). The absorbance of reactions at 410 nm was measured. Reactions were performed in quadruplicate. Error bars indicate ± standard error. C. Glucan phosphatase assay of immunoprecipitated FLAG-laforin. The absorbance of reactions at 620 nm was measured. Reactions were performed in quadruplicate. Error bars indicate ± standard error. Proteins are as indicated as in Figure 1B. The experiments above were performed a minimum of three times.