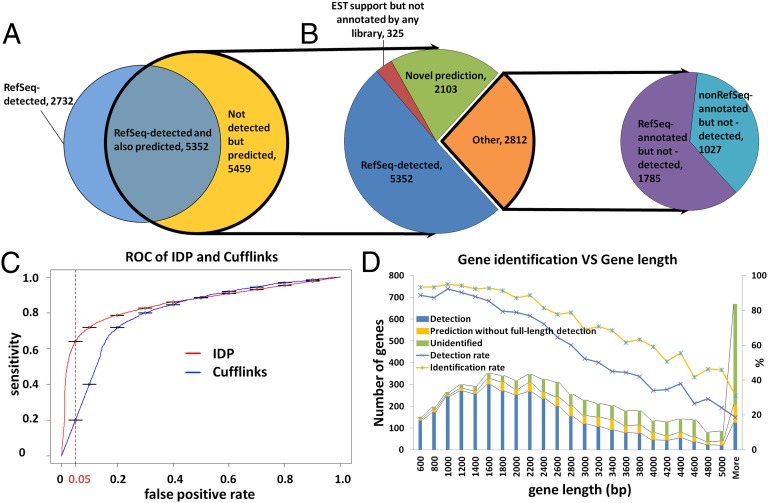
Fig. 1.
Gene isoform detection and prediction of hESCs (H1 cell line) by IDP. (A) Venn diagram of IDP detections and predictions (see introductory section for definition of detection and prediction). A total of 8,084 RefSeq isoforms are detected and highlighted in blue. A total of 10,811 predictions are highlighted in yellow and outlined with a thick black line. A total of 5,352 detections of RefSeq isoforms are also predicted by IDP. (B). Pie chart of annotated isoforms and novel isoforms in IDP predictions. IDP predictions rescue 1,785 RefSeq-annotated isoforms (in purple) that cannot be detected directly at full length. In addition, there are 1,027 predictions that are not annotated in RefSeq but are found in Ensembl, Known Genes, or GENCODE (cyan). Finally, 2,428 novel isoforms (green and red) are identified, 325 of which have EST support (red). (C) ROC performance analysis of IDP and Cufflinks. IDP predictions have much higher sensitivity in the acceptable FPR range from 5% to 10%. When FPR is controlled to 5%, the IDP prediction sensitivity is as high as ∼62%, whereas the corresponding Cufflinks sensitivity is only about 20%. (D) RefSeq gene identification rate decreases with the gene length. Combining detections and predictions, the overall identification rate by IDP is ∼73% (yellow line with blue star markers). IDP prediction rescues a significant number of isoforms from long genes that are not directly detected.