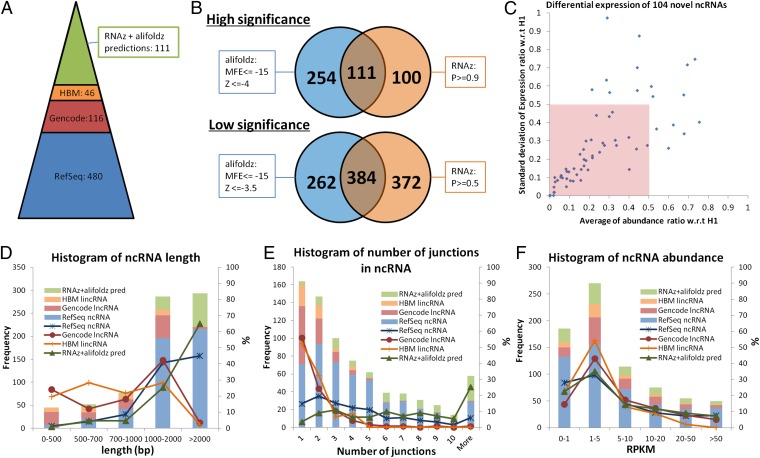
Fig. 9.
Noncoding RNA identification: the distributions of length, number of junctions, and abundance. (A) Annotated ncRNA identifications and novel ncRNA predictions. A total of 480 multiexon RefSeq-annotated ncRNAs are identified from H1. After filtering out RefSeq isoforms, the remaining IDP output contains 116 GENCODE-annotated lncRNAs. After filtering out RefSeq and GENCODE isoforms, 46 HBM lincRNAs are identified. The intersection of high-significance RNAz and alifoldz predictions of the remaining novel isoforms contains 111 putative ncRNAs. (B) RNAz and alifoldz are used to identify the ncRNA from 2,428 isoform predictions. Two stringency levels are suggested by the developers. For all subsequent analyses, we use the intersection of the high-stringency outputs from the two methods as our predicted ncRNAs. (C) Differential expressions of 104 novel ncRNAs w.r.t. H1. Seven of 111 novel ncRNA predictions are not included, because of insufficient short-read coverage in H1. Fifty novel ncRNAs (inside the pink box) have an averaged abundance ratio smaller than 0.5 with SD smaller than 0.5. (D) Length distribution of IDP-identified isoforms of RefSeq ncRNA, GENCODE lncRNA, HBM lincRNA, and RNAz/alifoldz predictions. (E) Distribution of number of junctions of IDP-identified isoforms of RefSeq ncRNA, GENCODE lncRNA, HBM lincRNA, and RNAz/alifoldz predictions. (F) Abundance distribution of IDP-identified isoforms of RefSeq ncRNA, GENCODE lncRNA, HBM lincRNA, and RNAz/alifoldz predictions.