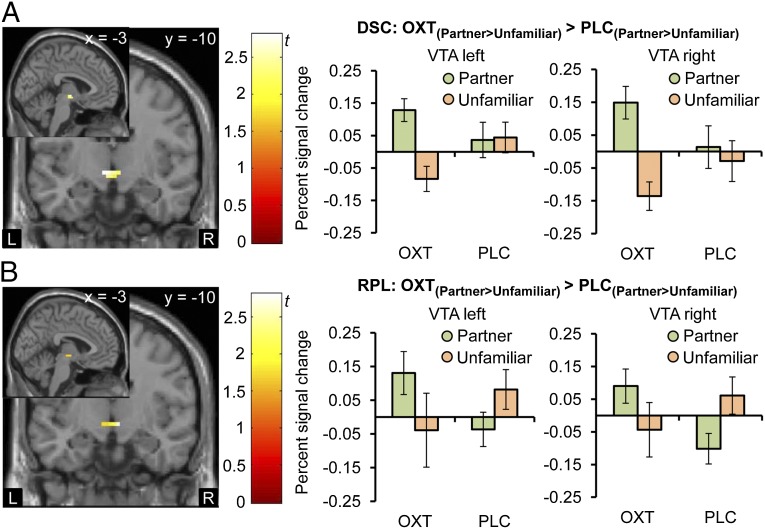
Fig. 3.
OXT effects on VTA responses. Both in the DSC (A) and RPL (B) study, the intranasal administration of OXT increased neural responses in the VTA to the face of the female partner compared with a matched, but unfamiliar woman (OXT(Partner > Unfamiliar) > PLC(Partner > Unfamiliar); DSC: left peak MNI coordinates −6, −10, −5; t(114) = 2.56, PFWE = 0.03; right peak MNI coordinates 0, −10, −5; t(114) = 2.33, PFWE = 0.051; RPL: left peak MNI coordinates 0, −16, −8; t(152) = 1.93, PFWE = 0.12; right peak MNI coordinates 6, −13, −5; t(152) = 2.89, PFWE = 0.02; display threshold P < 0.05 uncorrected). Analyses of percent signal change in the bilateral VTA showed the greatest response to the mate after OXT administration. Error bars indicate SEM. DSC, discovery; L, left hemisphere; OXT, oxytocin; PLC, placebo; R, right hemisphere; RPC, replication; VTA, ventral tegmental area.