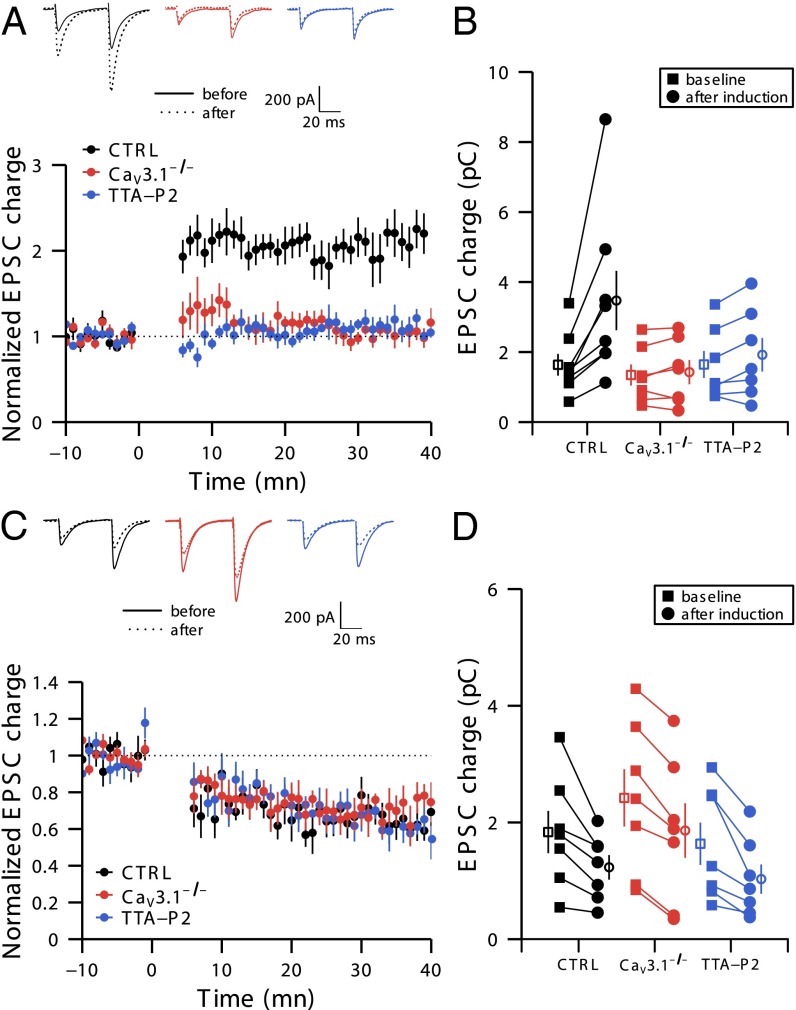
Fig. 1.
Activation of T-type calcium channels is necessary to induce PF–PC LTP but not for LTD. (A and B) T-type calcium channels are required for LTP induction. (A, Upper) Representative traces from 10 successive sweeps before and 30 min after induction of LTP. (A, Lower) Time course of normalized EPSC charge in control (black), in the continuous presence of 1 µM TTA-P2 (blue), and in CaV3.1−/− mice (red). The LTP induction protocol started at time 0. (B) EPSC charge before and 30 min after LTP induction. Filled symbols represent individual cells, whereas empty symbols represent means. Black, red, and blue indicate results from control mice, from CaV3.1−/− mice, and in the presence of TTA-P2, respectively, and corresponding n = 8, 7, and 7 individual experiments for the three sets of mice, each run on a different slice. Note that data from some cells are superimposed. (C and D) T-type calcium channels are not required for LTD induction. (C, Upper) Representative traces from 10 successive sweeps before and 30 min after induction of LTD. (C, Lower) Time course of normalized EPSC charge in control (black), 1 µM TTA-P2 (blue), and in CaV3.1−/− mice (red). The LTD induction protocol started at time 0. (D) EPSC charge before and 30 min after LTD induction. n = 7 individual experiments from different slices for the three sets of conditions.