Fig. 3.
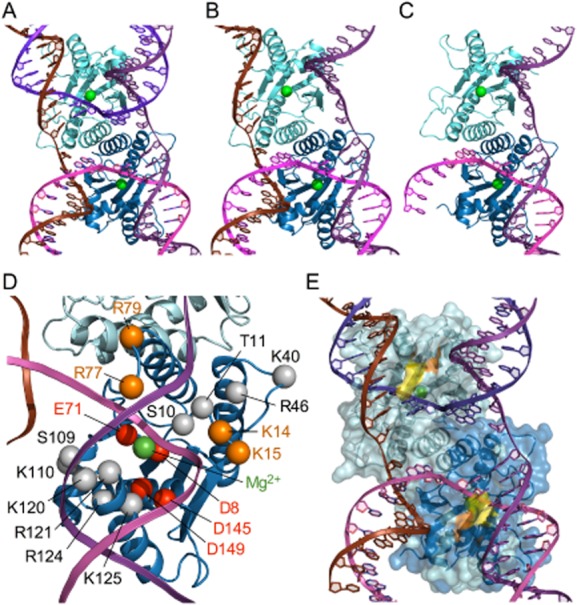
Models for 67RuvC bound to Holliday, flap and fork junctions.
A. A dimer of 67RuvC and a Holliday junction model based on that of the T4 endo VII-DNA complex (Biertumpfel et al., 2007). 67RuvC and DNA are shown in cartoon versions with the protein remote from the viewer with monomers coloured cyan and blue, bound Mg2+ cations as green spheres and the four strands of the DNA coloured brown, purple, magenta and violet with the trace of the phosphate backbone represented by a ribbon.
B. A model of a complex with a 3-stranded flap junction.
C. A model of a complex with a 2-stranded fork junction.
D. The locations of key residues within a monomer of 67RuvC. Alpha carbon positions are highlighted with spheres (grey for those residues mutated in this study; red for the catalytically important, cation binding residues and orange for other residues referred to in the text), labelled and shown relative to the modelled DNA as in Fig. 3A. The location of the bound Mg2+ cation is also shown with a green sphere.
E. A model of a complex with a 4-stranded Holliday junction highlighting the location of the R121A (yellow) and R124A (orange) mutants studied in vitro.
