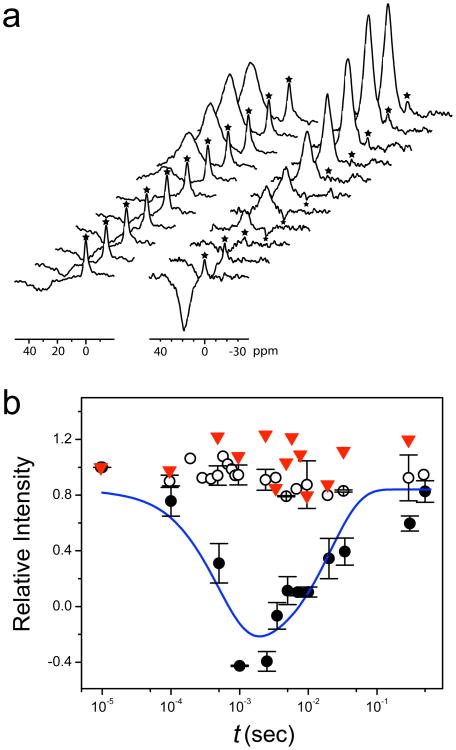
Figure 2. Channel functional measurements.
(a) Stack plots of 35Cl NMR spectra in Cl− flux measurements across largeunilamellar vesicles (LUV) by NMR magnetization inversion transfer (MIT) experiments (see Supplemental Information for experimental details). Left: control vesicles without the protein; Right: vesicles having the hGlyR-α1 TMD channels. The Cl− shift reagent Co(Gly)3− separates extra-vesicle Cl− signal from the intra-vesicle signal (marked by the asterisk *). The intensity of the intra-vesicle signal (*) changes as a function of the inversion-recovery time (t) due the exchange of intra- and extra-vesicle Cl−. (b) The rates of Cl− influx (ki) and efflux (ke) are determined by fitting the intensity changes as a function of t with a two-site exchange model (solid line, see fitting details in Supplemental Information). ○, LUV without protein; ●, LUV with protein; ▼, LUV with the same amount of protein and with 1 mM picrotoxin. Error bars show the standard error of the mean.