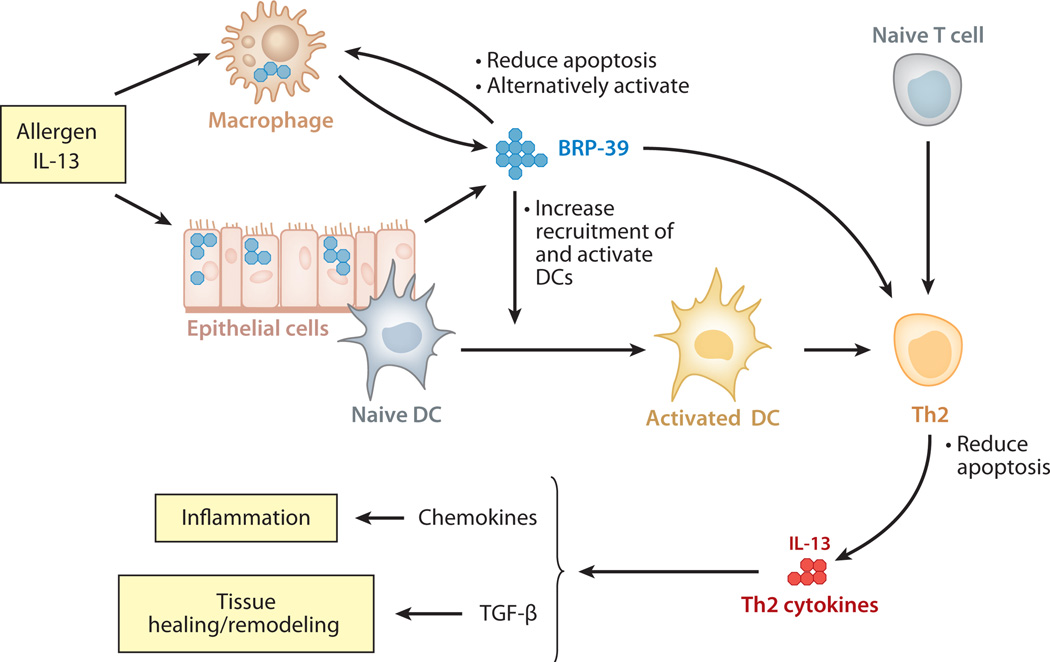
Figure 3.
Contributions of BRP-39/YKL-40 to allergen-induced Th2 inflammation and tissue remodeling. At sites of adaptive Th2 inflammation, cytokines such as interleukin (IL)-13 stimulate BRP-39/YKL-40 production in macrophages and epithelial cells. BRP-39/YKL-40, in turn, contribute to this response by preventing macrophage apoptosis and inducing alternative (M2) macrophage differentiation, by increasing the number of and activating local dendritic cells (DC), and by inhibiting Th2 cell apoptosis. The Th2 cytokines that are then produced induce chemokines and transforming growth factor (TGF)-β1, which contribute to inflammation, remodeling, and healing.