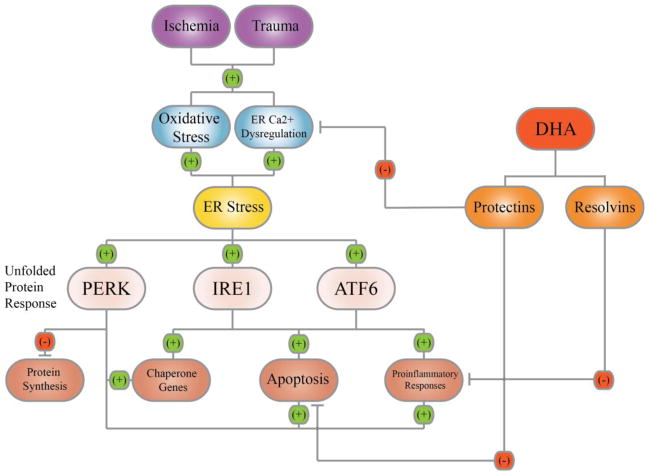
Figure 1. ER stress and DHA therapeutic potentials.
Ischemia and trauma injuries trigger ER stress via oxidative stress and/or ER Ca2+ dysregulation. ER stress leads to the activation of the PERK, IRE1, and ATF6 pathways that are collectively termed as the unfolded protein response. These pathways result in a global attenuation of protein synthesis, yet an increase in the synthesis of relevant chaperone proteins and ER-associated inflammation. Chronic ER stress and inflammation ultimately lead to apoptosis. The administration of DHA, through its bioactive derivatives, decreases ER Ca2+ dysregulation, can resolve inflammation, and decrease neuronal cell death.