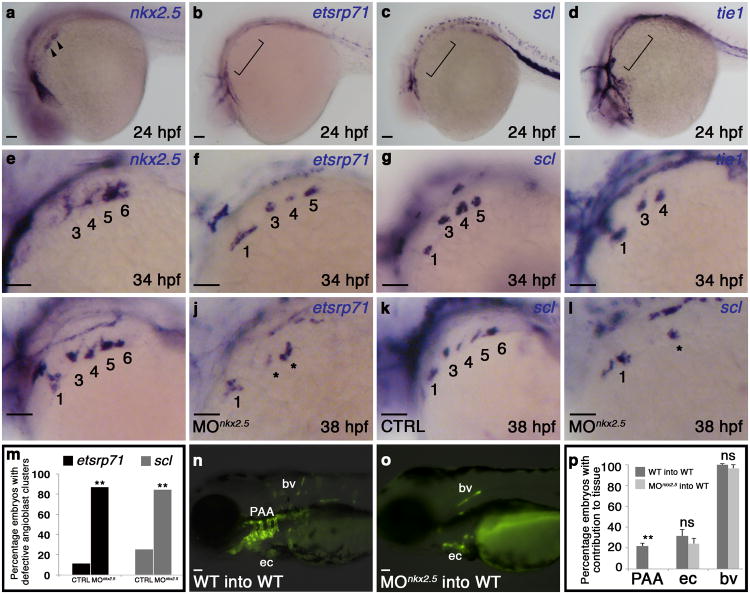
Figure 5. Cell-autonomous requirement for Nkx2.5 in promoting the PAA progenitor to angioblast transition.
a-h, in situ hybridization analysis of nkx2.5(a,e), etsrp71(b,f), scl(c,g), and tie1(d,h) at 24 (a-d) and 34 (e-h) hpf. i-letsrp(i,j) and scl(k,l) transcripts evaluated by in situ hybridization in control (CTRL; i,k) and nkx2.5 morphant (MOnkx2.5;j,l) embryos, asterisks mark abnormal PAAs 3-6, numbers are quantified in m. (etsrp CTRL n=61, MOnkx2.5 n=53, two-tailed t test **P=0.001 across two independent experiments; scl CTRL n=106, MOnkx2.5 n=116, two-tailed t test **P=0.001 across two independent experiments). n-p, WT (n) and MOnkx2.5(o) donor-derived GFP+ PAA endothelium in unlabelled WT hosts. p, Quantification of host embryos showing GFP+ donor cells from WT (n=208) or MOnkx2.5 (n=86) embryos in the PAAs, endocardium (ec), and body vasculature (bv). Fishers exact test, PAA two tailed **P=0.0001; ec two-tailed P=0.3239 (not significant, ns); bv two-tailed P=0.2710, across four independent experiments. Scale bar = 50μm. a-l, lateral views, anterior left; PAA islands indicated; a-h n>20 embryos per group; m,p, Error bars indicate one standard deviation.