Figure 5.
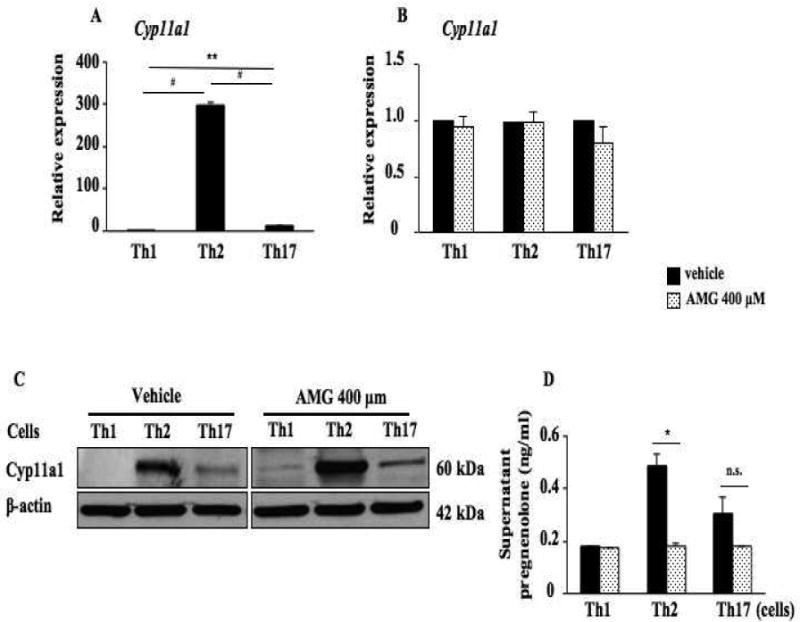
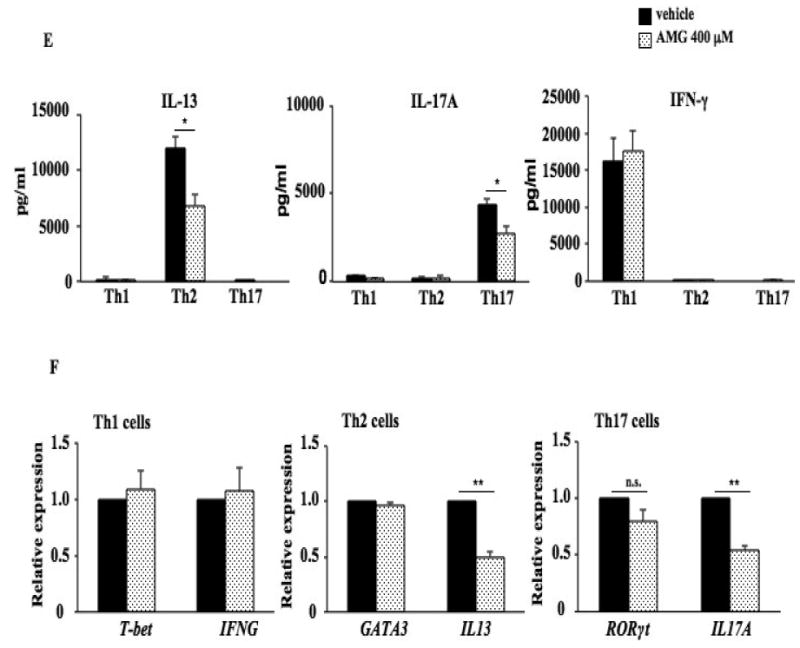
Inhibition of Cyp11a1 enzymatic activity suppresses the differentiation of naive CD4 T cells into Th2 and Th17 cells without affecting lineage-specific transcription factor and Cyp11a1 expression. (A). Relative Cyp11a1 expression in naive CD4 T cells differentiated in vitro into Th1, Th2, and Th17 cells from spleen of naive TCR-transgenic mice (OT II mice) determined by RT-PCR. (B). Cyp11a1 mRNA expression in polarized CD4 T cells in the presence of AMG or vehicle. (C). Western blot analysis of Cyp11a1 protein in polarized Th1, Th2, or Th17 cells treated with AMG or vehicle. (D). Pregnenolone levels were assessed in supernatants of cultured CD4 T cells under Th1, Th2, and Th17 polarizing conditions. (E) Cytokine levels in supernatants of cultured CD4 T cells treated with inhibitor or vehicle under Th1, Th2, and Th17 polarizing conditions. (F) Th1, Th2, and Th17 cytokine and lineage-specific transcription factor mRNA expression in polarized Th1, Th2, or Th17 cells treated with the inhibitor or vehicle. The data shown are from 3 independent experiments (n=12). *P<0.05, **P<0.01, #P<0.001, n.s. not significant.
