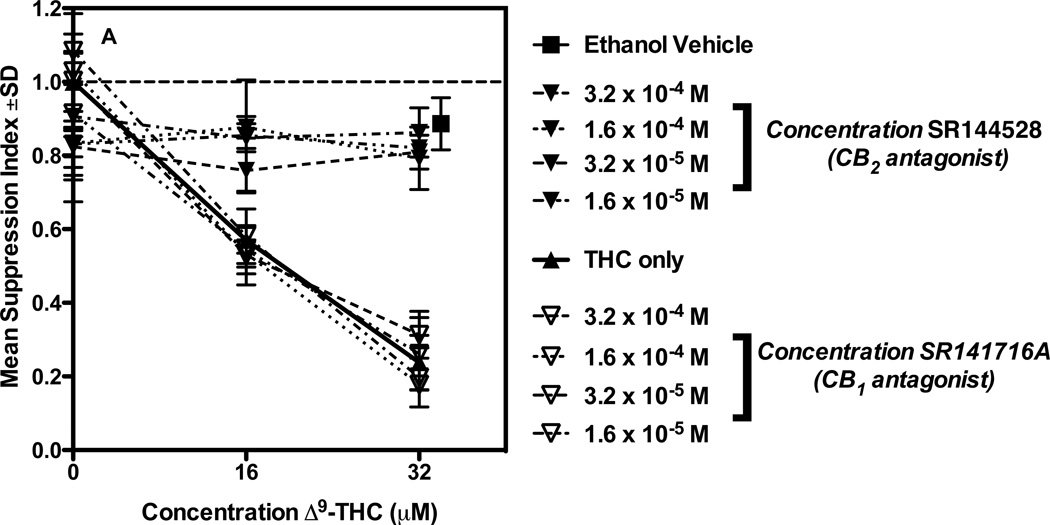
Fig. 2.
Δ9-THC and the CB2-selective agonists, JWH-015 and O-1966, inhibit the MLR via the CB2 receptor. C57BL/6 responder splenocytes were pretreated with varying concentrations of SR141716A, a CB1 antagonist, (▽), SR144528, a CB2 antagonist (▼), or ethanol vehicle (■) for 2 h. The cultures were then treated with one of three cannabinoids. Panel a: Δ9-THC (▲) or ethanol vehicle (■). Panel b: JWH-015 (◆) or ethanol vehicle (■). Panel c: O-1966 (●) or DMSO vehicle (□). Vehicle controls were the amount of ethanol needed to dissolve the antagonist (0.05% v/v) plus 0.4% v/v of ethanol (a,b) (■) or the amount of DMSO (c) (⊠), needed to dissolve 32 µM Δ9-THC, JWH-015 or O-1966. Data are mean ± S.D. of 3 separate experiments, with quadruplicate wells for each treatment. p < 0.001 (ANOVA, agonist + CB1 antagonist versus agonist alone, agonist + CB2 antagonist versus vehicle)