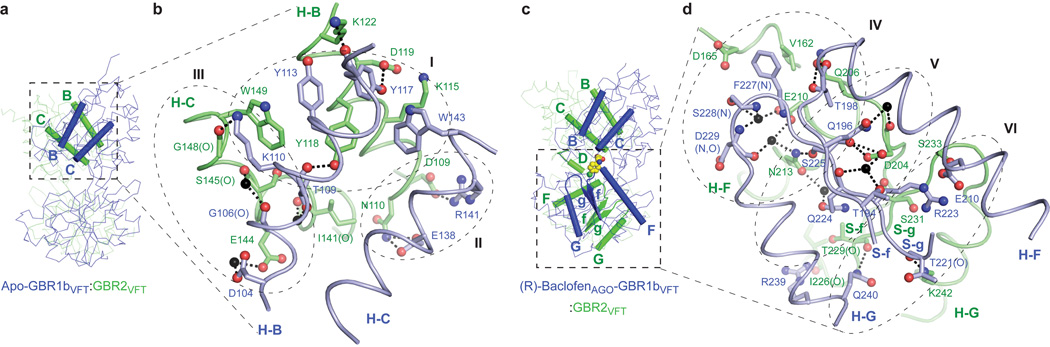
Figure 3. Heterodimer interface.
a, Structure of apo-GBR1bVFT:GBR2VFT with the elements involved in heterodimer formation highlighted by ribbons (LB1-LB1: B and C helices). b, Specific contacts at the LB1-LB1 heterodimer interface of apo-GBR1bVFT:GBR2VFT. The interface area is divided into three regions I, II, and III. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.
c, Structure of (R)-baclofenAGO-GBR1bVFT:GBR2VFT showing the elements involved in heterodimer formation (LB1-LB1: B and C helices; LB2-LB2: F and G helices, f and g strands, and connecting loops). d, Specific contacts at the LB2-LB2 heterodimer interface of (R)-baclofenAGO-GBR1bVFT:GBR2VFT. The interface area is divided into three regions IV, V, and VI. Dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds.