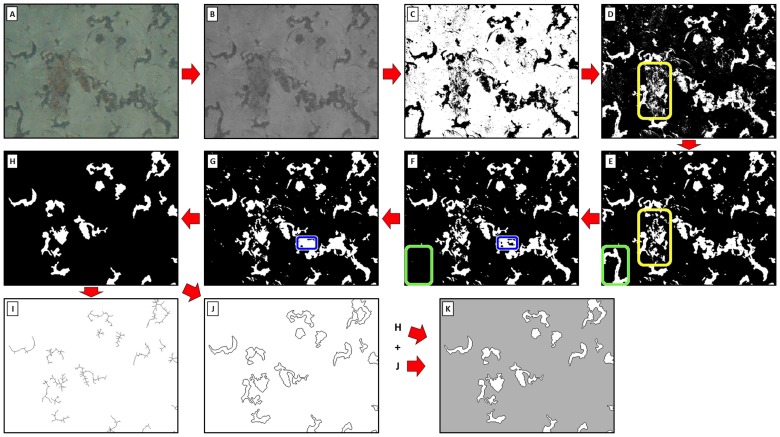
Figure 4. Steps of image processing of a MODS-culture photo.
(A) Original photo. (B) Conversion to gray scale, obtaining the ‘Gray scale image’. (C) Global binarization, transforming all the pixels in black (0) or white (1). (D) Black-white inversion. (E) Border smoothing, to reduce the ‘noise’. The yellow rectangle in figures D (before) and E (after) shows the changes produced by this process. (F) Exclusion of boundary objects, deleting the objects in the border of the photo. The green rectangle in figures E (before) and F (after) shows the changes produced by this process. (G) Holes Filtering, removing black objects inside white objects. The blue rectangle in figures F (before) and G (after) shows the changes produced by this process. (H) Area filtering, dropping the outsider values in the distribution of area values, obtaining the ‘Cleaned image’. (I) Skeletonization, obtaining the ‘SKL values’. (J) Identification of object borders, obtaining the ‘Borders image’. (K) Image recoloring: The black pixels in figure H are converted to gray, and this picture is superposed by the figure J, giving the ‘Tri-colored image’. Figures (B), (I) and (K) are used for the features extraction process.