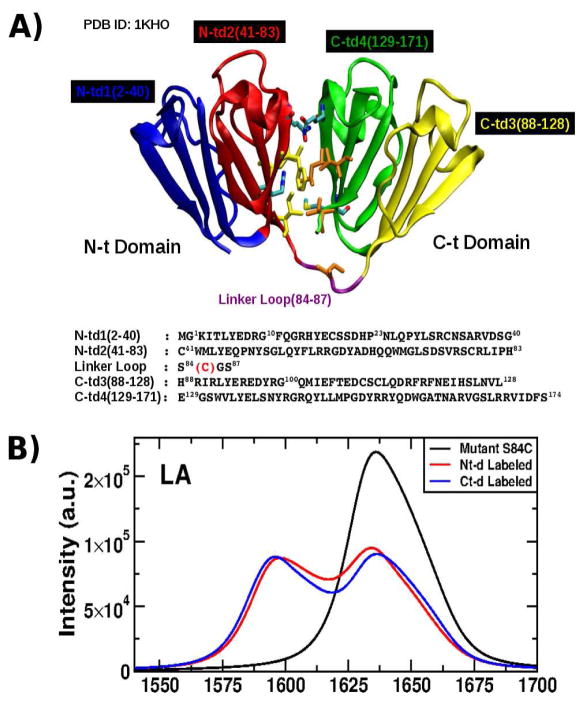
Figure 1.
A: Structure of the γD-Crystallin protein showing its four Greek Motifs divided into the two domains Nt (blue and red) and Ct (green and yellow) connected by a loop (purple) and their respective sequence as shown in the crystal structure (PDB ID: 1KHO) with the mutation S84C indicated (red). Residues located in the interdomains (in licorice) are responsible in the stability of the entire structure. B: Linear absorption (LA) (top) in the infrared regime of the mutant S84C-HγD-Crystallin for the full sequence (black), N-td labeled (red) and C-td labeled (blue).