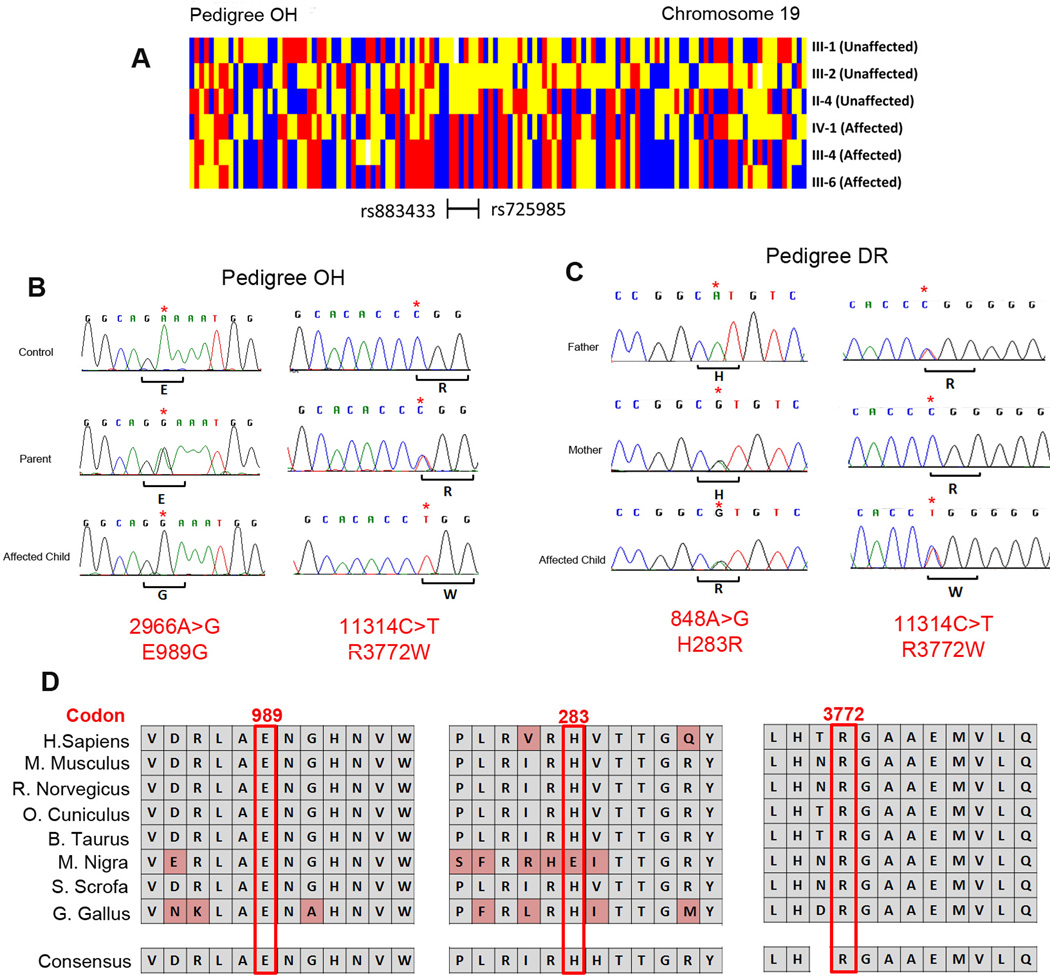
Figure 2. Homozygosity mapping and mutation analysis.
(A) Schematic showing regions of shared homozygosity on chromosome 19 in pedigree OH created by genotypes from individuals III:1, III:2, II:4, IV:1, III: 4 and III:6 by dChip software.22 Red or blue denotes homozygous AA or BB; yellow denotes heterozygous AB, and white denotes absent call. The homozygous region shared by the 3 affected children and no parent is bordered by single nucleotide markers rs725985 and rs886466. (B) Sanger sequencing chromatograms from an unrelated control individual (top), and from an unaffected parent (middle) and affected child (bottom) of pedigree OH. Note that the parent is heterozygous and the affected children are homozygous for RYR1 c.2966A>G (left) and RYR1 c.11314C>T (right) nucleotide substitutions. The wild-type and the predicted amino acid substitutions are provided below each sequence. (C) Sanger sequencing chromatograms from unaffected father (top), unaffected mother (middle) and an affected child (bottom) of pedigree DR. The father has wild-type sequence at RYR1 c.848 and a heterozygous RYR1 11314C>T nucleotide substitution, the mother has a heterozygous RYR1 848A>G nucleotide substitution and is wild-type at RYR1 c.11314. The affected child is heterozygous at both nucleotides. The wild-type and the predicted amino acid substitutions provided below each sequence. (D) Evolutionary conservation of RYR1 glutamic acid 989, histidine 283 and arginine 3772 residues in 8 species.