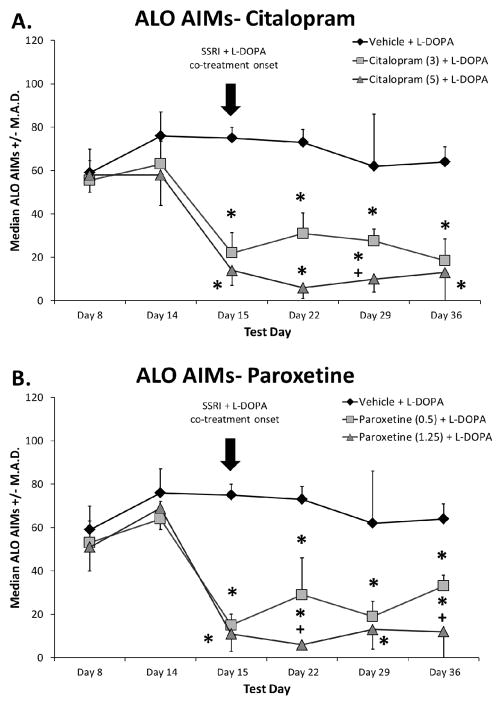
Fig. 1.
Effects of prolonged selective 5-HT reuptake inhibitors citalopram (A) and paroxetine (B) on the expression of established L-DOPA-induced abnormal involuntary movements (AIMs). Rats were L-DOPA-primed for 14 days and axial, limb, and orolingual (ALO) AIMs were recorded on days Prime 8 and Prime 14. Thereafter, equally dyskinetic groups were treated with vehicle, citalopram (3 or 5 mg/kg, s.c.), or paroxetine (0.5 or 1.25 mg/kg, s.c.) 30 min prior to L-DOPA (6 mg/kg, s.c.) + benserazide (15 mg/kg, s.c.) daily for 22 days. The arrow indicates the start of SSRI and L-DOPA co-treatment. ALO AIMs were evaluated for 3 h after L-DOPA on days 15, 22, 29, and 36. Values are expressed as medians (AIMs ± median absolute difference; M.A.D.). Significant differences were determined by non-parametric Kruskal-Wallis ANOVAs at each test day with Mann-Whitney post-hocs. * p < 0.05 vs. Vehicle + L-DOPA, + p < 0.05 vs. Citalopram (3) or Paroxetine (0.5) + L-DOPA.