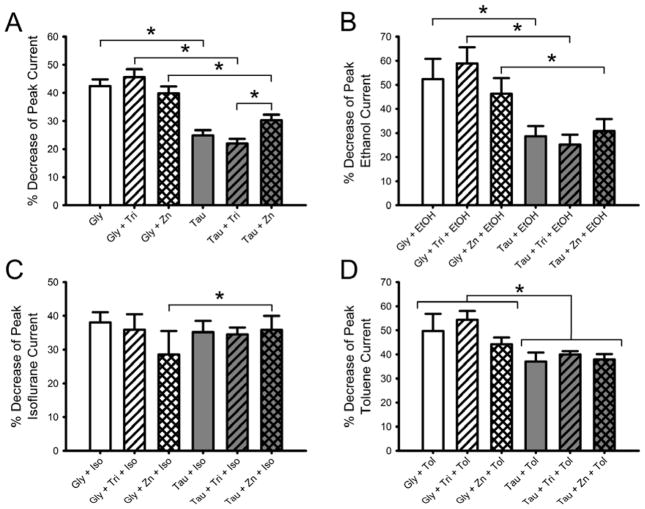
Fig. 7.
Zn2+ levels do not significantly affect desensitization of glycine- or taurine-activated glycine receptors. A) Zn2+ does not affect the rate of desensitization produced by maximally-effective concentrations of glycine or taurine. Percent decrease in peak current observed 5 s post-peak is graphed for each agonist/Zn2+ level combination. Data are shown as mean + S.E.M. of 26–35 oocytes. B) Zn2+ and ethanol do not affect the rate of desensitization produced by maximally-effective concentrations of glycine or taurine. Percent decrease in peak current seen 5 s post-peak in the presence of 200 mM ethanol is graphed for each agonist/Zn2+ level combination. Data are shown as mean + S.E.M. of 6 oocytes. C) Zn2+ levels have no effect on isoflurane changes in desensitization rates of taurine-activated glycine receptor currents. Percent decrease in peak current observed 5 s post peak in the presence of 0.55 mM isoflurane is graphed for each agonist/Zn2+ level combination. Data are shown as mean + S.E.M. of 6 oocytes. D) Zn2+ and toluene do not interact to affect desensitization rates of maximally-effective concentrations of glycine and taurine. Percent decrease in peak current seen 5 s post-peak in the presence of 0.42 mM toluene is graphed for each agonist/Zn2+ level combination. Data are shown as mean + S.E.M. of 5 oocytes. *, p < 0.05.