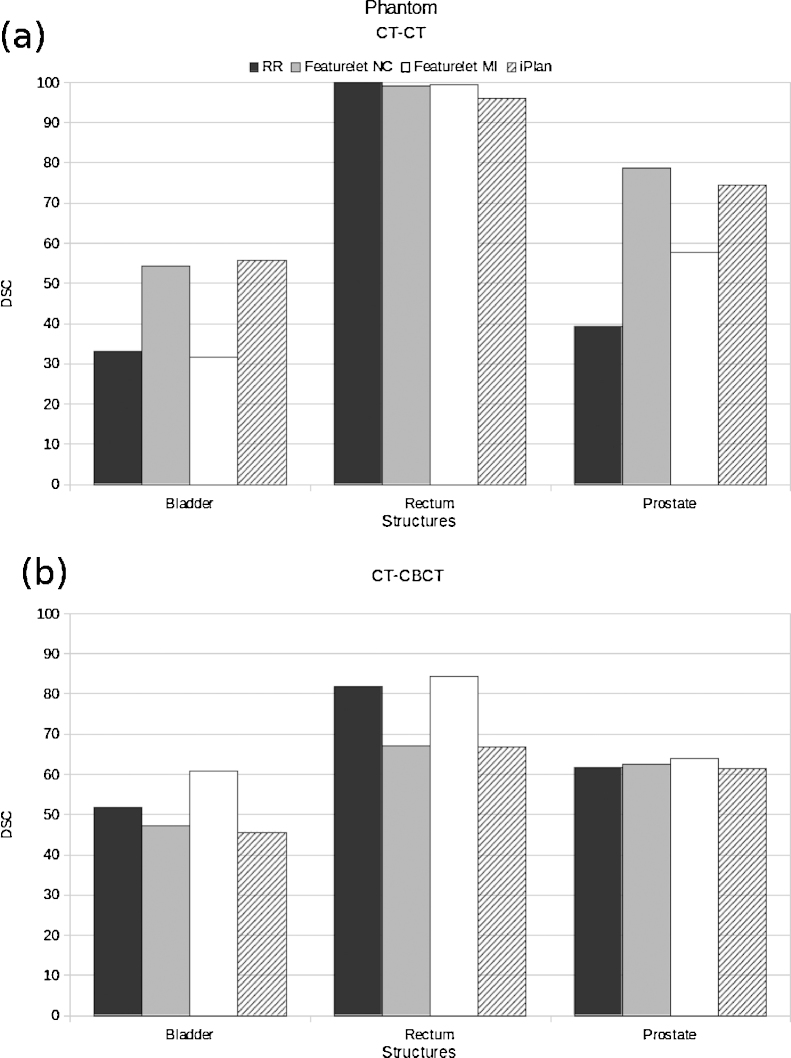
Figure 4.
(a) DSC values for the phantom CT-CT deformable registration; here, two deformations are included. It can be seen that on average the featureletNC method and the iPlan method had a similar performance. The featureletMI method is not improving the DSC substantially. (b) DSC values for the phantom CT-CBCT deformable registration. Here, three deformations are included. For both bladder and rectum, the featureletNC and iPlan methods are reducing the DSC value, and almost not changing it for the prostate. On the other hand, for the three structures the featureletMI method is improving the DSC. RR corresponds to the rigid registration starting point, featureletNC to the featurelet deformable registration method using normalized correlation metric, featureletMI to the featurelet deformable registration method using mutual information metric and iPlan corresponds to the deformable registration performed using the iPlan -adaptive application.