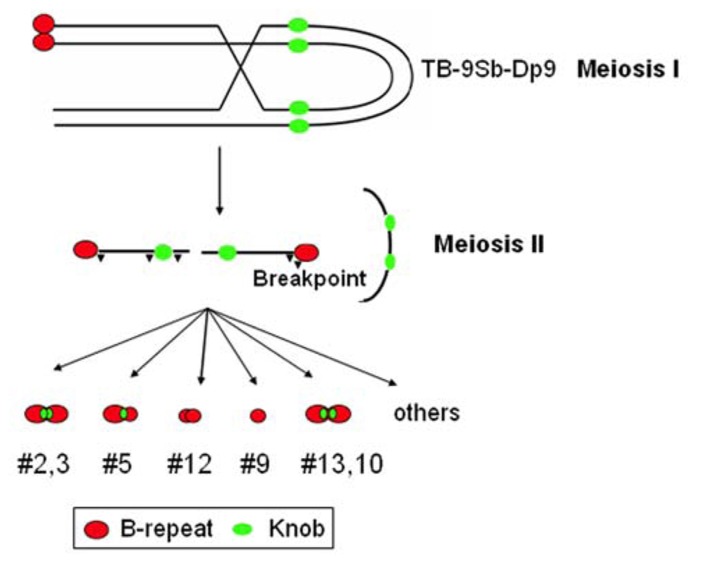
FIGURE 1.
Initiating the chromosome type BFB cycle to generate minichromosomes. A translocation between the B chromosome and the short arm of chromosome 9, TB-9Sb, was recombined with a reverse duplication of 9S to generate TB-9Sb-Dp9. This chromosome can recombine with itself as depicted which will join the sister centromeres. At meiosis II the sister centromeres will separate and create a chromatin bridge that will rupture. This broken chromosome will fuse, form a bridge, and break through the gametophyte generation but at the second pollen mitosis the B centromere will undergo non-disjunction. This will place two broken chromosomes in a sperm and thus following the subsequent fertilization event, these two broken chromosomes will set up the chromosome type of BFB cycle that will continue throughout development. Using this approach, Zheng et al. (1999) and Han et al. (2007) produced a collection of minichromosomes described in the text. B repeat is the B chromosome specific sequence present in and around the centromere of the B chromosome. Knob is the repeats of heterochromatin found on maize chromosomes including the short arm of chromosome 9.