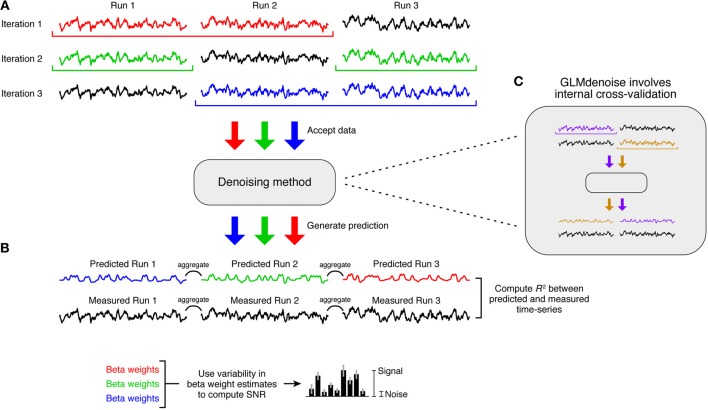
Figure 3.
The Denoise Benchmark (DNB). We designed an architecture that enables automatic evaluation of a candidate denoising method. (A) Cross-validation accuracy. Leave-one-run-out cross-validation is used to quantify the accuracy of the denoising method. In each iteration of this procedure, the denoising method is trained on all runs except one and is asked to predict the task-related signal in the left-out run. Predictions are aggregated across the left-out runs, and the accuracy of the predictions is quantified using coefficient of determination (R2). (B) Signal-to-noise ratio (SNR). Variability of beta weight estimates across the cross-validation iterations is used to estimate SNR. (C) Candidate denoising methods. Any denoising method that conforms to the prescribed application programming interface (API) can be evaluated in the DNB architecture. Note that the cross-validation used in the DNB is distinct from any internal resampling scheme that might be used by a denoising method (such as the cross-validation used within GLMdenoise).