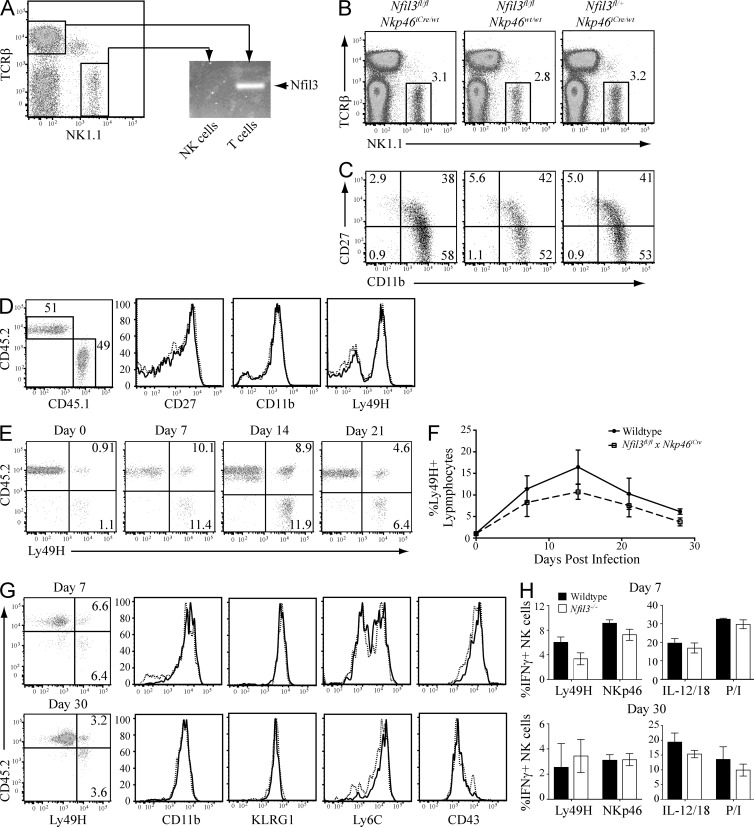
Figure 8.
Nfil3 is not required for NK cell maturation and function beyond the early NK cell progenitor stage. (A) NK cells and T cells were sorted from Nfil3fl/fl × Nkp46iCre mice and Nfil3 expression was analyzed by PCR. (B) Percentage of mature NK cells was determined in Nfil3fl/fl × Nkp46iCre mice and littermate controls. (C) Expression of maturation markers CD27 and CD11b was determined on NK cells from Nfil3fl/fl × Nkp46iCre mice and littermate controls. (D) Mixed bone marrow chimeric mice were generated using a 1:1 ratio of bone marrow from WT (CD45.1, solid lines) and Nfil3fl/fl × Nkp46iCre (CD45.2, dotted lines) donor mice. Percentages of donor cells and expression of CD27, CD11b, and Ly49H was determined by flow cytometry at 8 wk after irradiation and reconstitution. (E and F) Splenic NK cells were purified from chimeric mice generated in D and adoptively transferred to Ly49h−/− hosts. Percentages of Ly49H+ NK cells were determined at indicated time points after MCMV infection. (G) Ly49H+ NK cells from MCMV-infected WT (solid lines) and Nfil3fl/fl × NKp46iCre (dotted lines) mice were analyzed for expression of the indicated molecules at days 7 (top) and 30 (bottom) PI. (H) The NK cells from G were stimulated for 5 h with anti-Ly49H, anti-NKp46, IL-12 + IL-18, or PMA + Ionomycin (P/I) and evaluated for IFN-γ production by flow cytometry. Error bars for all graphs show SEM and all data are representative of n = 3–4 mice per group per time point, repeated in three independent experiments.