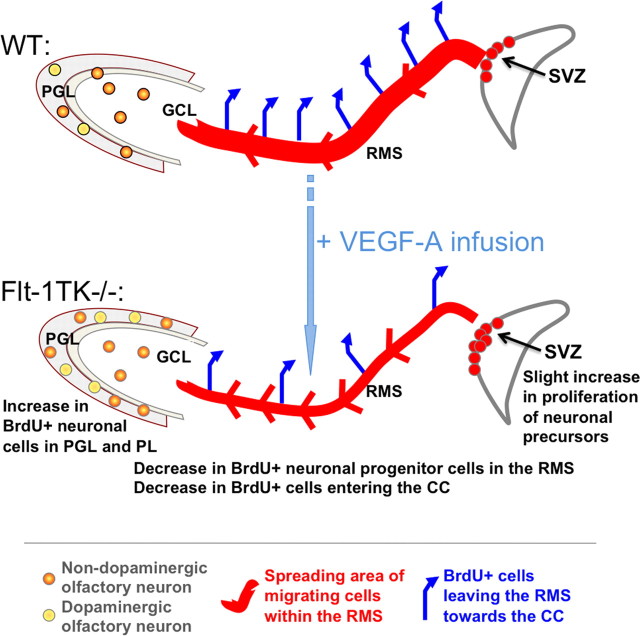
Figure 9.
Schematic drawing of the differences observed in the steps of neurogenesis between WT and Flt-1TK−/− mice. Olfactory neurons derive from NPCs of the SVZ. Flt-1TK−/− display higher proliferation rates of DCX+ cells in the aSVZ. Our data point toward a faster migration, which accounts for the fact that, in Flt-1TK−/− at day 6, there are already fewer BrdU-labeled NPCs in the RMS than in WT mice. In addition, during migration, the spreading of BrdU-labeled cells in Flt-1Tk−/− is smaller than in controls. Once in the OB, the cells detach and migrate as single cells into the different layers of the OB. In Flt-1TK−/− mice, significantly more cells migrate through the PL into the PGL than in WT mice. In addition, more neurons form in the PGL of Flt-1TK−/− and especially more neurons of a dopaminergic subtype when compared with WT mice. As a result of their constant increase in neurogenesis the OB of the Flt-1TK−/− mice is bigger in size than that of controls. Infusion of VEGF-A into the LV of WT mice during the migration period was sufficient to induce the migration phenotype observed in Flt-1TK−/− mice.