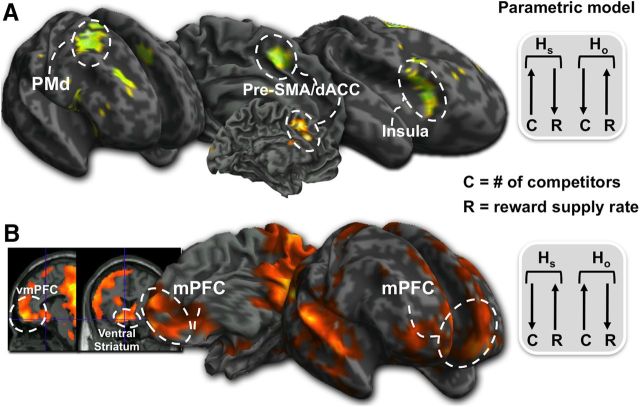
Figure 2.
Parametric analysis of brain activation associated with changing competition (C) and reward frequency (R). A, dACC, AI, dorsal premotor cortex (PMd), and pre-SMA activity when C increased and R decreased in the subject's own habitat (HS) compared with the other habitat (HO). B, vmPFC, ventral caudate, and dorsal caudate when C decreased and R increased in HS relative to HO. This suggests that preparatory motor areas come online more when it is disadvantageous to be in the HS while staying in HS due to low C and high R activates the mPFC and ventral caudate.