Figure 6.
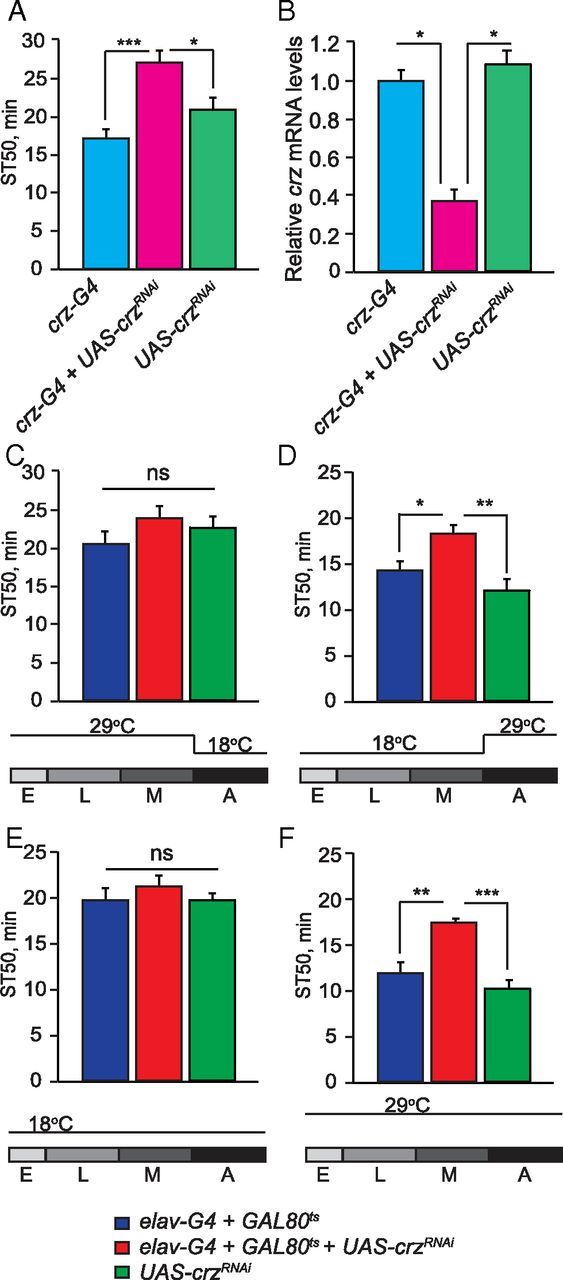
The neuropeptide Crz mediates ethanol sedation sensitivity. A, RNAi knockdown of crz specifically in crz-expressing neurons reduces ethanol sedation sensitivity. ST50 values of flies in which UAS-crzRNAi is driven with crz-GAL4 (crz-GAL4/UAS-crzRNAi/+) differ significantly from the GAL4 (crz-GAL4/+) and UAS (UAS-crzRNAi/+) control flies (one-way ANOVA, Tukey–Kramer post hoc, n = 16). B, Expression of crz upon RNAi knockdown. Flies with neuronal knockdown of crz by RNAi, specifically in crz-expressing neurons (crz-GAL4/UAS-crzRNAi/+), showed a 62% reduction of crz transcript levels compared with the GAL4 (crz-GAL4/+) and UAS (UAS-crzRNAi/+) control flies (one-way ANOVA, Tukey–Kramer post hoc, n = 3). C, D, Temporal knockdown of crz expression was achieved by coexpressing UAS-crzRNAi with elavc155-GAL4;tub-GAL80ts. Flies were raised at 29 (GAL4 on, GAL80ts off) and 18°C (GAL4 off; GAL80ts on). ST50 values are shown for the experimental group with temporal inhibition of crz expression (elavc155-GAL4;tub-GAL80ts/UAS-crzRNAi), and the GAL4-GAL80ts (elavc155-GAL4;tub-GAL80ts /+), and UAS (UAS-crzRNAi /+) controls. C, Neuronal inhibition of crz expression during development does not alter ethanol sedation sensitivity. (p > 0.05, n = 12). Flies were raised at 29°C then shifted to 18°C at eclosion until behavioral testing. D, Neuronal inhibition of crz expression during adulthood reduces ethanol sedation sensitivity (one-way ANOVA, Tukey–Kramer post hoc, n = 12). Flies were raised at 18°C then shifted to 29°C from the time of adult eclosion until behavioral testing. E, F, Temperature shift controls. E, Raising flies at 18°C during both development and adulthood (GAL4 off) leads to normal ethanol sedation sensitivity. (p > 0.05, n = 12). F, Raising flies at 29°C during both development and adulthood (GAL4 on) leads to decreased ethanol sedation sensitivity (one-way ANOVA, Tukey–Kramer post hoc, n = 16).
