Figure 3.
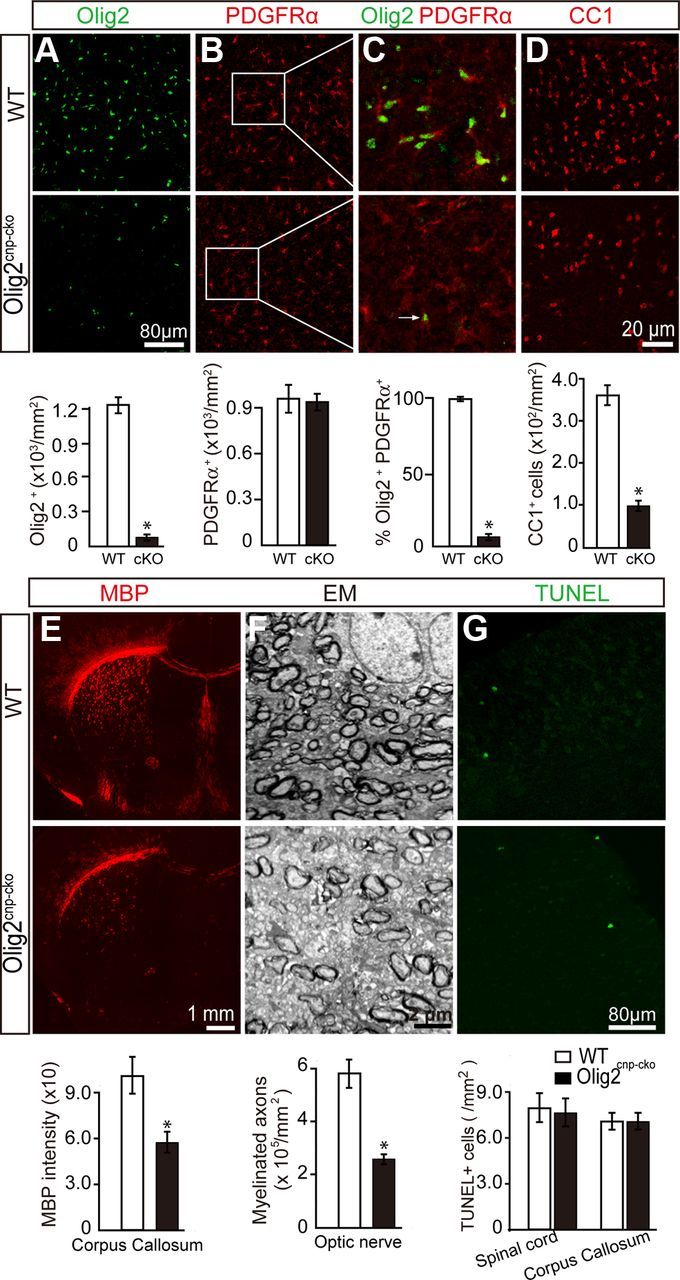
Deletion of Olig2 in OPCs inhibits oligodendroglial differentiation and myelination. Olig2 was specifically deleted in OPCs by crossing Olig2flox/flox mice with CNPcre/+ mice to generate the Olig2cnp-cko mice. Spinal cord sections of wt mice and Olig2cnp-cko mice at P0 were stained for Olig2 (A, green) and PDGFRα (B, red) confirming decreased levels of Olig2+ cells and the deletion of Olig2 in the majority of PDGFRα+ OPCs (C, 3% of PDGFRα+ cells coexpressed Olig2). D, Immunostaining of P14 spinal cord sections shows an 80% decrease in CC1+ cell numbers in the Olig2cnp-cko mice without changing the TUNEL+ apoptotic cell numbers in either spinal cord or corpus callosum (G). E, P14 coronal brain sections of wt and Olig2cnp-cko mice stained for MBP (red) show a 45% reduction of MBP expression in the knock-out mice. F, Optic nerve electron microscopic images of Olig2cnp-cko and wt mice at P21 reveal less myelinated axons in the absence of Olig2 in OPCs. Scale bars: A, B, G, 80 μm; C, D, 20 μm; E, 1 mm; F, 2 μm. Data are mean ± SEM (5 animals in each group). *p < 0.05.
