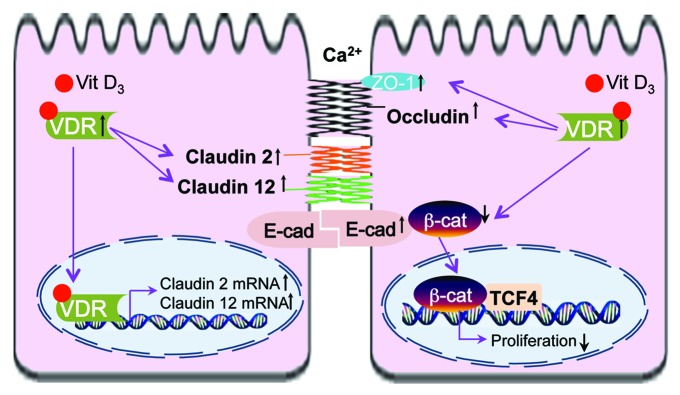
Figure 1. VDR and cell adhesion/TJs of epithelial cells. Activation of VDR suppresses the activity of β‑catenin, thus deceasing nuclear β-catenin, suppressing transcriptional factor T cell factor (TCF) and inhibiting cell proliferation. Increased VDR level is also associated with increased claudin2 and 12, which may play roles in calcium homeostasis and barrier function. The other cell junction proteins involved in the vitamin D/VDR include E-cadherin, Occludin and ZO-1.
