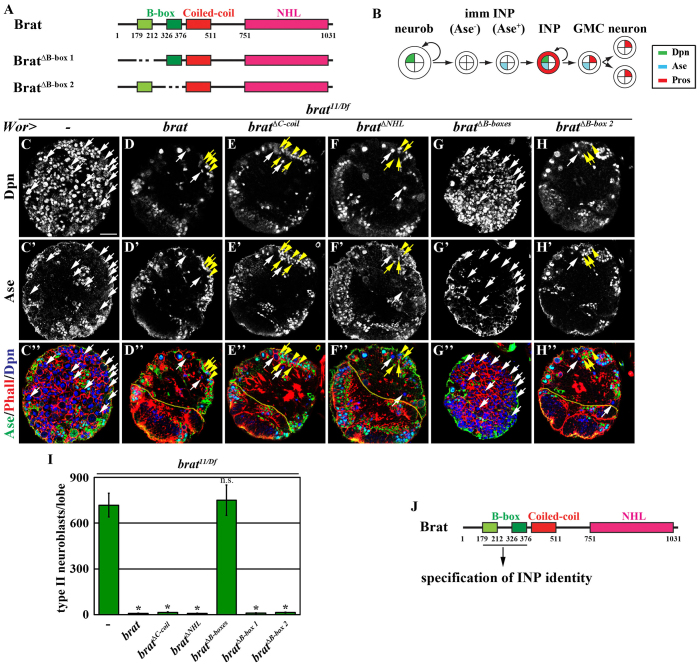
Fig. 2.
The B-boxes of Brat function uniquely in the specification of INP identity. (A) Summary of the UAS-brat transgenes used to test for B-box redundancy in the rescue of supernumerary neuroblasts in brat null brains. (B) Summary of the cell types in the type II neuroblast lineage in the Drosophila larval brain. Dpn, Deadpan; Ase, Asense; Pros, Prospero; GMC, ganglion mother cell; INP, intermediate neural progenitor; imm INP, immature INP; neurob, neuroblast. (C-H′) Overexpression of full-length brat, bratΔC-coil, bratΔNHL or bratΔB-box 2 rescues the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat null brains, but overexpression of bratΔB-boxes does not. The effects on the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat mutant brains were determined based on total type II neuroblasts per brain lobe. The dotted line separates the brain from the optic lobe where both are visible in the optical section. White arrows, type II neuroblasts (Dpn+ Ase-); yellow arrows, Ase-immature INPs (Dpn- Ase-) and Ase+ immature INPs (Dpn- Ase+); yellow arrowheads, INPs (Dpn+ Ase+). (I) Quantification of total type II neuroblasts per brain lobe in brat mutant brains overexpressing various Brat transgenic proteins. Error bars indicate standard deviation of the mean (s.d.). *P<0.05 versus control (Student’s t-test). (J) Summary of the domain required for Brat-dependent specification of INP identity. Scale bar: 20 μm.