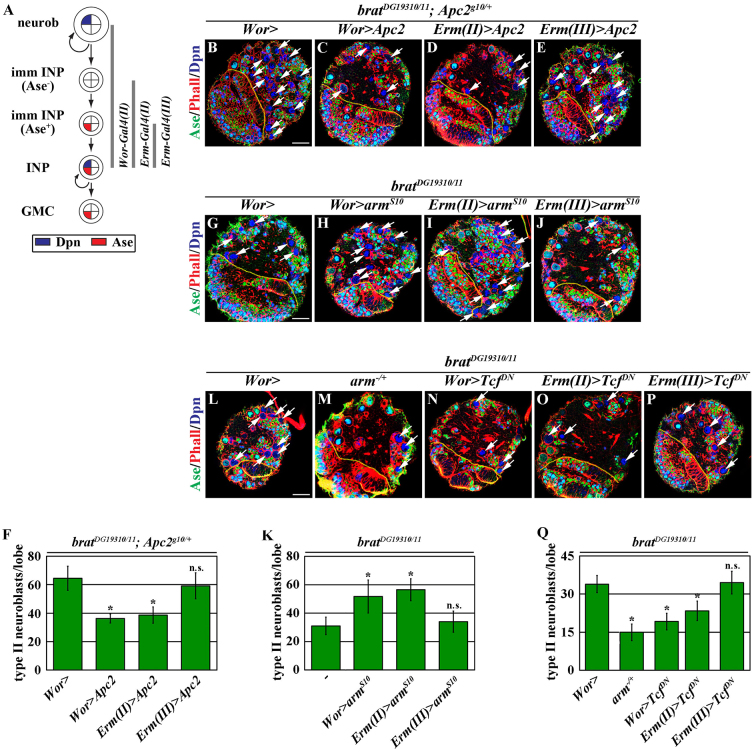
Fig. 5.
Brat specifies INP identity by antagonizing Arm-dependent gene transcription in immature INPs. (A) Summary of the expression patterns of the Gal4 drivers within the type II neuroblast lineage (Xiao et al., 2012). (B-E) Increased function of Apc2 early in the lineage suppresses the enhancement of the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat mutant brains induced by Apc2 heterozygosity. (F) Quantification of total type II neuroblasts per brain lobe in brat mutant brains. (G-J) Increased function of arm early in the lineage enhances the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat mutant brains. (K) Quantification of total type II neuroblasts per brain lobe in brat mutant brains. (L-P) Decreased arm function via arm gene heterozygosity or overexpression of TcfDN in type II neuroblasts or Ase- immature INPs suppresses the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat mutant brains. By contrast, overexpression of TcfDN in Ase+ immature INPs does not suppress the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat mutant brains. (Q) Quantification of total type II neuroblasts per brain lobe in brat mutant brains. Error bars indicate s.d. *P<0.05 versus control (Student’s t-test). See Fig. 2 for description of labels. Scale bars: 20 μm.