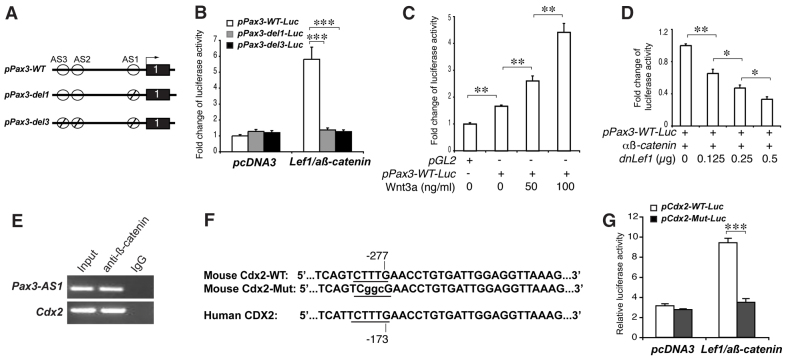
Fig. 4.
Transcriptional activation of Pax3 and Cdx2 promoters by Wnt/β-catenin signaling. (A) Three putative Tcf/Lef1 binding activation sites (AS1-AS3) are present in the presumptive 5′ promoter region of the Pax3 gene. The intact (WT) or deletions (ϕ) of the activation sites are indicated. (B) Luciferase reporter assays demonstrate the specific activation of the promoter with the wild-type, but not the deletion, of AS1 or AS1-AS3 after co-transfection with Lef1 and active β-catenin (aß-catenin) cDNAs. (C) The dose-dependent activation of the Pax3 promoter treated with various amounts of Wnt3a protein. (D) The dose-dependent repression of the intact Pax3 promoter activity by dominant-negative (dn) Lef1. (E) Chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrates the specific recruitment of the Pax3 AS1 or the Cdx2 promoter region by β-catenin antibodies, but not the non-specific IgG, from wild-type caudal neural tubes of E9.5 mouse embryos. (F) The wild-type and mutated Tcf/Lef1 binding sites in the mouse Cdx2 promoter region, which is conserved in the human CDX2 gene. (G) Luciferase reporter assays demonstrate the specific activation of the Cdx2 promoter with the wild-type, but not the mutated, Tcf/Lef1 binding site by β-catenin signaling. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Error bars indicate s.e.m.